...
| Info | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
The main body of the text is here, but links have not been completed. |
There are two versions of the Manual as well as the 'on-line' version. |
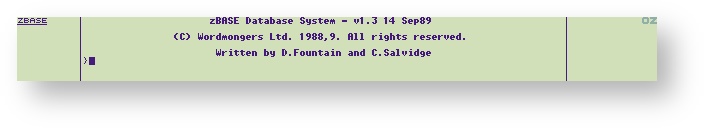
About Wordmongers Limited
WORDMONGERS LIMITED 1989
...
| The original Wordmongers 32K EPROM had a S/No label that covered the erasing window. |
Downloads
| View file | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Wordmongers zBASE
Database suite for Z88
Manual zbman1 v0.02 190888
zBASE v1
| View file | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
A Microsoft Word version with thanks to Detlef Obermann,
...
This application need 32K of either EPROM or Flash space.
Introduction
zBASE is a ROM based application package for the Cambridge Computer Z88 portable. It is a database that allows users store information easily.
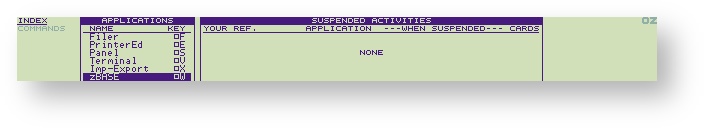
Selecting zBASE
zBASE can be started from the INDEX using the cursor bar or can be selected at any time using W. If zBASE has already been used it will appear in the SUSPENDED ACTIVITIES area of the index from which it can be re-selected using the cursor bar.
...
The same is true of the Help screen.
WORDMONGERS LIMITED
| View file | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Wordmongers zBASE
Database suite for Z88
Manual zbman1 v0.02 190888
zBASE v1
An introduction to databases | |||
| Files | Records | Fields | Data types |
| Index key fields | |||
How to create a data file | |||
| Defining fields, width, type | Creating the file within zBASE | Opening and closing database files | Checking structure |
Indexing | |||
| To create the index file | Using FIND | Adding data to an indexed file | Tech note re INDEX file sizes |
Retrieving data | |||
Entering data | |||
| At curly prompt | Variables and Top Bit Characters | Using command (do) file | |
Amending data | |||
| At curly prompt | Using command files | Deleting data | |
Selection and control | |||
| At curly prompt | LOCATE FOR | LIST [FOR | DISPLAY [FOR |
| Using command files | |||
Manipulating data files | |||
| COPY TO filename [PD] [FOR <cond>] [DELIMITED] [FOR <cond>] | APPEND FROM filename | COPY TO filename <[STRUC- TURE] / [PD]> | COPY TO <filename> STRUC- TURE |
| Using command files | Deleting data | Selection and control | Manipulating data files |
Moving around a file | |||
| SKIP | GO (TO RECORD NUMBER ..) <expression> | GO TOP, GO BOTTOM | |
ENVIRONMENTAL COMMANDS | |||
| -ESC- ON/OFF | SET ECHO | ||
Indirect variables | |||
| &memvar | &numericvar | ||
zBASE output to printer port | |||
Z88 output facilities | |||
| n+ P | n+ S | ||
System Limits | |||
Precedence of operators | |||
Using multiple databases | |||
Importing files from PD | |||
Using Z88 popdowns | |||
SECTION B | |||
zBASE Commands | |||
| conventions | keywords | commands | functions |
zBASE Functions | |||
SECTION C | |||
zBASE Programs | |||
| Sample programs | Stock Control System | ||
Foreword
Congratulations on choosing zBASE. The Z88 Portable offers a wide range of built-in facilities. With the addition of zBASE, the Z88 comes of age.
...
Complete application systems can now be written for the Z88 by people other than professional programmers.
Acknowledgement & Thanks
...
R.Beddard, Ian Braby, Mike Case, Tony Cox, G.C.Denney, John Dobson, R.C.Dorrance, Steve Drain, John Driver, Vic Gerhardi, C.M.Glover, S.P.Gray, F. W. Halliday, Gerald Hughes, B. P. James, Robin Jarvis, Charles Jenkins, N. A. Joseph, Dr Warren Kovach, Chris Lewis, Thomas Malinowski, M. Meijeraan, Francis Musgrave, M. Parker, Dr. L. Ratnasabapathy, C. M. Robinson, S.Fraas, K.G.Woolf, Roy Woodward, Matthew Soar, H.E.Shaw and John Hudson.
zBASE Quick start guide
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| 96010404 |
| 96010404 |
| 96010404 |
| 96010404 |
| QSG5 |
| 96010404 | QSG7 | QSG8 |
| QSG9 |
| 96010404 | QSG11 |
| 96010404 | ||
| QSG13 | QSG13.1 | QSG13.2 |
Getting familiar with a new piece of software is often tedious and sometimes daunting. To provide a Quick demonstration to those who are new to zBASE, this Quick start guide is a short tutorial aimed at providing a rapid introduction to the system.
...
This guide is no substitute for reading the manual. Indeed, this guide will merely scratch the surface of zBASE capabilities. However, since zBASE needs liveware to make use of those capabilities, it is important to the authors that the liveware should feel some early reward for the effort of getting familiar with zBASE. Those rewards are plentiful in this guide.
QSG1
With the INDEX on display on the Z88, open the clear perspex cover labelled '1 2 3', and insert the zBASE Application ROM in slot 2. Close the perspex cover. (See the Fitting & Using the ROM.)
The menu bar should be moved on the APPLICATIONS INDEX until it is highlighting the zBASE application.
Press to run zBASE.
QSG2
When the } symbol, known as the curly prompt appears, type the word QUIT followed by . This action ends the use of zBASE. In version 1.2 you need to confirm the return to the APPLICATIONS INDEX, by pressing any key.
This is the only proper way to exit from zBASE. If the key is used, and the zBASE suspended application is KILLed, open database files will not be properly closed and permanent damage will occur to the data files.
QSG3
The first real job is to create a data file. To do this, the file structure must be defined. This definition is done in PipeDream. Highlight the PipeDream application and press . This creates a new PipeDream suspended application.
QSG4
Type in the following lines, exactly as shown.
...
Now press FS, followed by the file name, PHBOOK.DEF. Then move the cursor down 4 lines using the ò, to the question, 'Save plain text'. Enter a Y for YES and hit .
QSG5
That has created the definition file for a phone book database. Now return to zBASE by pressing W.
...
Database open in 1: is PH.DBF
COMP STRING 15
PHONE STRING 17
NAME STRING 20
KEYFIELD STRING 5
62 bytes/rec
QSG6
Now create an INDEX file for easy searches.
...
That will establish an index file for use later.
QSG7
Data input
After creating the file, the next step is to enter data. To begin with, the method shown will be the simple way of storing information. QSG13 below sets out two examples of how command files can make such work easier.
...
}APPEND BLANK
}LET 1:COMP$=" "
}LET 1:PHONE$="020-7833-1212"
}LET 1:NAME$="Insp Bond"
}LET 1:KEYFIELD$="Bond"
}APPEND BLANK
}LET 1:COMP$="Short Brothers"
}LET 1:PHONE$="01494 885555"
}LET 1:NAME$="Morris Short"
}LET 1:KEYFIELD$="Short"
QSG8
With at least a few records entered, a FIND process is required. This may be done directly at the curly prompt, or as for appending, by means of a command file as described in Indirect variables.
The zBASE command to use on an index file is 'FIND'.
...
Note that only the first FOUR characters of any command need be used.
QSG9
Looking for matches in an UNINDEXED file.
...
NB. The key used must be the one on the left of the keyboard. (No we don't know why either.)
QSG10
To close the file, enter
}USE
To re-open the file type
}USE PH.DBF INDEX PH.NDX
QSG11
To check whether a file is open, type
}DISP STATUS
To check a file structure, enter
}DISP STRUCTURE
QSG12
To return to the Z88 APPLICATIONS INDEX, enter
}QUIT.
NB. IT IS IMPORTANT THAT THE QUIT COMMAND IS USED AS THE METHOD OF CLOSING zBASE. If zBASE is KILLed as a suspended application, loss of data will occur because the files will not be properly closed.
QSG13
zBASE programs - two startup examples.
QSG13.1
An alternative method of entering data is to write a command file that makes it all a bit easier.
...
Type or load the program labelled PHENT.PRG96010404. Do not use characters. The lines that start with an ASTERISK (*) are comment lines that are ignored by zBASE. They do not have to be typed in at all.
After typing in PHENT.PRG it should now be saved. Press FS, enter the filename PHENT.PRG, 4 lines and enter Y to save the file as PLAIN TEXT.
Back in PipeDream, after the file save, enter W to return to zBASE. When back at the } prompt, type the following
...
[If zBASE was QUIT rather than left suspended, the database file with its index must be re-opened before running PHENT.PRG. If this is the case, see QSG9 above for guidance on re-opening the file.]
...
A few more records should be entered to give the database something to get its teeth into.
QSG13.2
FINDing using a command file.
As before for PHENT.PRG, start a new PipeDream document and type or load in the program labelled FPROG.
Save this file using FS. Use a filename of say FPROG. Remember it must be saved as PLAIN TEXT.
Return to zBASE either through the Z88 APPLICATIONS INDEX, or by simply pressing W.
...
This quick start guide has been designed to provide new users with an opportunity to get something out of zBASE quickly. It does not reveal the flexibility available in zBASE nor does it demonstrates the wide potential for this database management program. The rest of the manual does go much further into the commands and functions contained in zBASE. Please take some time to review the rest of the manual and so enjoy the further capabilities of your Z88/zBASE combination.
zBASE Manual
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| 96010404 | ||
| Manual conventions | Important basic concepts | Database areas |
| 96010404 |
| Interactive versus Command file |
The Quick Start Guide is designed to be a brief exposure to the major facilities of zBASE. Those new to database languages may find this a very useful starting point.
Section A of this manual, 'Introduction to zBASE', describes zBASE in descriptive terms with some examples of how the system can be used. Commands are dealt with in an order that are likely to appeal to a first time database user.
Section B - 'zBASE Reference', is an alphabetical list of the zBASE commands, with the syntax for each one dealt with separately. Following that, the zBASE functions are dealt with in similar fashion.
Section C - 'Sample Programs and Glossary', contains some sample programs that can be written in the zBASE language with a brief Glossary that explains some of the terms used in the manual. Also shown is a series of zBASE programs that together form a Stock Check system,
Introduction
The Wordmongers zBASE suite is designed to provide general database management opportunities for the expanded Z88. The Z88 must have at least a 128K RAM expansion cartridge in slot 1.
...
Alternately, regularly used sets of commands may be put together into a command file to save repeated entering of the same commands. Those familiar with the dBASE family of programs from Ashton-Tate will find that there are some marked similarities between zBASE and dBASE II. (See trademark notice)
Copyright & Trademark notices
See Copyright & Trademark notices
Disclaimer
See Disclaimer
Handling, ROM's & installing the software
zBASE will only run on an expanded Z88. This means that the Z88 must have at least a 128K RAM cartridge installed. If a single RAM is fitted, it must be in slot 1.
...
To run zBASE, move the cursor to the zBASE application option in the INDEX and hit , or enter W.
Manual conventions
See Manual conventions
Important basic concepts
zBASE is a command driven database language with over 40 commands and functions. This provides a powerful facility for programming the Z88 for data manipulation. To those familiar with dBASE II, the granddaddy database program, there should be a feeling of having seen it all before. Given that imitation is the most sincere form of flattery, these similarities are purely intentional. However, for a variety of reasons, not least of which is a 32K ROM space, not all dBASE II facilities are emulated. Equally, some have been altered in an attempt to improve and to provide a better fit with the Z88.
Certain elements of the zBASE system need to be explained early on. These elements relate to the use of variables and files.
Database areas
Data files may be opened in either of two areas. These areas are called PRIMARY and SECONDARY. These areas are labelled as 1: and 2: respectively.
The 1: and 2: symbols are referred to elsewhere in this manual as the usage area. Whenever a field variable is addressed, it must be prefixed with this usage area symbol. The single exception to this is in the use of a field's list in the LIST and DISPLAY commands.
Variables
Variables are either memory variables or field variables. A memory variable is a label for a pigeon hole containing a number or a string of letters. Such memory variables or MVARS are volatile. They exist only for as long as the zBASE program is in use. When zBASE is QUIT, memory variables are lost. When zBASE is left as a suspended application, memory variables remain preserved along with the rest of the program.
...
Field variables are treated just like memory variables except they have a 1: or 2: in front of their name to distinguish them.
Interactive versus Command file
zBASE operates in two different modes. One is called the interactive mode and the other is command file driven.
...
In command file mode, a set of zBASE commands are put together in a PipeDream plain text file. At the curly prompt, the command DO FRED will call the file called FRED and will execute the commands found in that file.
...
If it is present, the file ZBRUN will be run automatically when zBASE is started. It acts like a BOOT.CLI file.
An introduction to databases
The following sections describe the building of a database file and its interrogation. It should be read through to the end. However, computer users are notorious for skipping manual pages. In this case, all the available commands with their syntax are explained in Section B and those wishing to learn by their mistakes are invited to use that section of the manual.
In this Introduction section, an example will be used to demonstrate techniques and commands. The system is a video tape cataloguing system. It is designed to keep track of a domestic video tape library in a fashion similar to that used for books. The specific command programs used can be found in - zBASE Programs.
Files
A database file is a collection of records. Each record contains details of 1 item, e.g. a library database file would contain separate records for each book in the library. A phone book might have one record per person recorded. In a Video Library system, each record would represent a single programme or film.
...
Many database systems assign file name extensions that show what type of file it is, i.e. file.DBF shows that the file is a DATABASE File. file.NDX would be an INDEX file. This is only a convention as far as zBASE is concerned and does not need to be regarded as a rule. Having said that, some form of file name convention is useful and the sample system for Stock Control, contained in Section Cof the manual does name all command file programs with an extension of .PRG.
zBASE database files contain certain information at the top of the file that is not readable by PipeDream. Therefore zBASE data files should not be opened under PipeDream. If this does occur then the file should not, under any circumstances, be SAVED from PipeDream. It should be KILLed. If it is saved from PipeDream, the header information will be destroyed.
Records
The limit on the number of records in a database in zBASE is 65535 records.
Each record in a database consists of different fields of information.
Fields
In designing a database, much of the effort is in getting the field structure correct for the required application. The classic consideration is whether to split a name into surname and forename or to hold the whole name as a single field.
...
Although this appears elementary in the case of name fields, it is nevertheless an important consideration whatever is being stored in the file.
Data types
There are two types of data, strings and numbers. Strings are simply collections of letters and or numbers that are to be regarded as TEXT. Numbers are numeric values upon which some form of calculation may be required.
...
Similarly, a phone number is made up solely of digits but because they are not involved in calculations they are usually held as STRING fields.
Index key fields
Strictly speaking this is not a different data type. However, it is a significant consideration when designing databases so is noted here as a consideration to be included in such a design.
...
An index key field can be any string field. If the file to be indexed is expected to be large, the index field should be kept as small as possible. This then means that the index file created is as small as possible and the time taken for a rapid search is also as small as possible.
How to create a data file
| Defining fields, width, type | Creating the file within zBASE | Opening and closing database files | Checking structure |
Having worked out the fields required in the database, the process of creating that file under zBASE starts with PipeDream.
...
Firstly, a PipeDream document is created defining the fields and their widths. This document is saved as PLAIN TEXT.
From within zBASE itself, the CREATE command is then invoked. Each step is described in more detail below.
Defining fields, width, type
From the Z88 INDEX, use the cursor to access PipeDream by moving the cursor to the PipeDream application and pressing . A new PipeDream document will be opened.
...
The pattern to note for defining file structures is explained in more detail in Section B - zBASE Reference. In short, each line contains details of an individual field. If the field is a string field the name must end with a $, it must be followed by a comma and must end with a number defining the width of the field. A numeric field is simply described with its name and no $ and no width.
Having defined the file structure, it must be saved. Press FS, followed by a file name, say VIDEO.DEF. Move the ò 4 lines to the Save plain text prompt and enter <Y>. The key will then save this structure file in a form to be accessed by zBASE in the next stage.
Creating the file within zBASE
Returning to zBASE, the next stage occurs at the curly prompt.
...
If data is ready for input, the file should be left open. To store data to the file, the fields are treated in a fashion very similar to memory variables. The only difference is that field variables from files are preceded by a 1: or 2:. (See Section 1 above or Section B later.)
The choice of where a file is opened is managed by the SELECT command. (See INTRO part 17 and Section B of the manual.) For the moment, assuming the SELECT command has not been used, the assumed area of operation is PRIMARY, labelled 1:.
...
Further APPEND BLANK commands may be used to add more records.
Opening and closing database files
To open a database file, the command word is USE. e.g.
...
That means that the current database area is area 1. See using multiple databases for further information about database areas.
...
Apart from the USE command, the QUIT command will also close all files before going back to the Z88 applications menu.
Checking structure
A command is available to display the structure of the currently open file. The command is
}DISPLAY STRUCTURE
Database open in 1: is VIDEO
REF_NUM STRING 3
TITLE STRING 20
TYPE STRING 3
TAPE_NO STRING 3
DURATION STRING 5
RATING STRING 1
42 bytes/rec
Indexing and Index files
In the Stock control system contained in Section C, the usual method of finding a product is by its code. Therefore, the file will be indexed on the CODE$ field.
To create the index file
some space must be freed in order to minimise the total memory used by zBASE. In this context, the space used is the database area 2.
...
The LIST and DISPLAY commands will both access the INDEX file for the order in which the display is to take place.
Using FIND
Use of the FIND command with an INDEXed file is the fastest way to search for a specific record. FINDing a record rapidly is achieved with an INDEX file as follows.
...
In command files, whenever a FIND is carried out, the next line should test for EOF()=0. If it is 0 (FALSE), then a match has been found.
Adding data to an indexed file
The fact that a file is indexed makes no difference to the adding of data except that a time allowance must be made for the updating of the index file.
...
Equally, if an INDEX file is open and an APPEND FROM command is used, the INDEX file be properly updated.
Tech note re INDEX file sizes
Given the Z88 environment, it is imperative that the amount of memory grabbed by zBASE should be kept to a minimum. This is to reflect the Z88 use of memory for all its functions and the ability to leave zBASE as a suspended application. If this is to be possible, it must use only a minimum of memory.
...
It also means that a file of say 250 records could be indexed very quickly even with a keyfield of say 20 characters.
Retrieving data
Apart from the FIND method described above, there is another way of finding particular pieces of information. This is by the use of a zBASE command called LOCATE which can search on any field. This is compared with FIND which only operates on the designated key field.
...
When used in conjunction with an indexed file, the DISP and LIST commands are very powerful. The FIND command is used to arrive at the first occurrence of the required value, then the DISP or LIST command, with its condition, can be used to show all the records which match, from that point in the file to the end.
Entering data
...
At curly prompt
APPEND BLANK
This command literally means add a blank record to the database file. It creates an empty record at the bottom of the database file in use in the currently selected area. Each field starts empty. Numeric fields start with a 0 (zero).
...
Another APPEND BLANK would immediately open another blank record ready for the next item.
Variables and Top Bit Characters
It is possible to have any name stored in a field of a zBASE record by using the decimal code of a character: For example:
...
An alternative method is to use a program called 'APPEND.PRG'. This routine emulates the dBASE APPEND command. The database to which data are to be amended must be open in area 1. TheAPPEND.PRG program must have been typed in under PipeDream and saved as PLAIN TEXT. At the } prompt, enter
}DO APPEND.PRG
...
For those who have no wish to get involved with zBASE program writing, the structure of APPEND.PRG is of no importance. It is offered as a short hand way of easily entering data to any database. See the introduction to Section C for details of how to obtain this and the other programs on a Z88 EPROM. download or on a floppy disk.
Using command (do) file
Within a command file, the APPEND BLANK command is still the only way to get a new record added to a file. However, a complete input screen may be devised using the AT SAY GET commands. This system provides the opportunity to have an input screen with proper prompts which automatically puts the data into the file without the repeated use of LET.
...
The next section is a blow by blow analysis of the input routine called, VIDINP.PRG.
* VIDINP.PRG V1.00 By Derek Fountain
CLS
SELE 1
USE VIDEO
...
The '* FLAG A' command line may be safely ignored at this stage. In the section below dealing with the use of multiple databases, this line is changed to something else to provide for additional related input.
...
With this program there is no message to the operator saying how to exit from the routine. As a first step in programming it might be a useful exercise to introduce a message saying 'Leave tape number blank to exit'. Alternatively, a different DO WHILE loop might be used to that a prompt could appear at the bottom of the program asking if there were more videos to be entered. If the response were 'N', the DO WHILE could be made to fail and so return control to the calling program or the curly prompt.
Amending data (Changing values, deleting records)
At curly prompt
Amending data is the same operation as entering data. The same LET command is used and the new data overwrites the old.
...
Tech note: The field variables from the current record are held in a temporary buffer while being manipulated. When the record pointer is moved, with a SKIP, GO, FIND, LOCATE or any other command which moves the pointer, that buffer is written back to the file. The file is not closed until a USE is issued or a QUIT. Therefore, if a fault happens when a file is open, some loss of data may occur.
Using command files
Within a command file, the GET command will be the more common method of changing variable values. If a variable contains non-blank data, that data will be displayed when the GET command is issued. That data may then be over-typed and replaced with the required new data. e.g.
...
A good example of an amending routine is SCSTOCK.PRG. It is part of the Stock Check system.
Deleting data
As with many database programs, deletion of data is done in a two part step. In the first stage, any records to be deleted are marked as such using the DELETE RECORD command. At a later time, when convenient, the file is copied across to a second file, leaving out the records marked for deletion.
...
The newly created file VIDEO will only contain those records which were not marked for deletion.
See also the PACK.PRG file.
Selection and control
One of the prime functions of a database language is not only to facilitate easy input and amending of data, but also easy retrieval of selected bits of the data.
The following commands show how such retrieval works.
At curly prompt
FIND <"field value">
FIND <memory variable>
LOCATE FOR <condition>
CONTINUE
LIST [FOR <condition>] [FIELDS <fieldname,fieldname>]
DISPLAY [FOR <condition>] [FIELDS <fieldname,fieldname>]
...
The curly prompt will not return immediately because the DISPLAY command is not intelligent enough to realise that an indexed file is in use. It continues searching the rest of the file for more hits. The --ESC- key stop the searching at any point.
LOCATE FOR .. CONTINUE
This command searches the file sequentially from the first record to the bottom of the file.
...
Having found a hit, the CONTINUE command will continue the search on the same basis. The search will continue from the current record to the bottom of the file.
LIST [FOR <condition>] [FIELDS <fieldname,fieldname>]
DISPLAY [FOR <condition>] [FIELDS <fieldname,fieldname>]
These two commands are very similar except that the DISPLAY command will only display records 7 at a time whereas the LIST command will scroll through all the hits without stopping.
...
}LIST FOR 1:TYPE$="COM" FIELDS TYPE$,TITLE$,TAPE_NO$
In command files
The DISPLAY, LIST and ? may be used within a command file in order to provide structured output to the screen. The operator may be prompted to input the piece of data to be matched and the command file could then display that data in a structured fashion.
...
AT line, 2 say 1:REF_NUM$
AT line,10 say 1:TITLE$
AT line,32 say 1:TYPE$
AT line,37 say 1:TAPE_NO$
AT line,42 say 1:DURATION$
LET line=line+1
CONTINUE
ENDDO
AT line,1 say "End of file found."
RETURN
See also SCSIFIND.PRG.
Manipulating data files
| COPY TO filename [PD] [FOR <cond>] [DELIMITED] [FOR <cond>] | APPEND FROM filename | COPY TO filename <[STRUC- TURE] / [PD]> | COPY TO <filename> STRUC- TURE |
Data is collected for a variety of reasons. Sometimes its like an antique collection with bits of information collected so long ago that there is no relevance to that data. However, assuming the data is to be used, it must be available in different forms. This is especially true on the Z88 when it will often be used as a temporary home for data to be transferred to another micro.
...
PipeDream format, with the PD option at the end of the line, would create a file with each record on a line with characters between fields. To load the file in PipeDream it must be loaded as Plain Text. Any fields of width greater than 12 will appear to be condensed. They are still there but the individual column widths will have to be reset to the required width in order to get all the data to appear.
...
Delimited means that the file is created for access by PipeDream with each record separated by a carriage return and each field is separated by a comma (,). This format is of particular interest to those wishing to export data to other database systems outside the Z88. Programs like dBASE II, III, IV and WordStar can use comma delimited files as raw data.
COPY TO filename [PD] [FOR <cond>][DELIMITED] [FOR <cond>]
COPY TO <filename> This version creates a straight copy of the file in zBASE format. e.g.
...
The whole file is copied to a PipeDream column format to be loaded as Plain text and the column widths adjusted as explained in the introduction to this section.
...
The resulting VIDCOM file, when loaded as PLAIN TEXT under PipeDream, would look like this:
...
If the file to be copied to has been created previously, the COPY TO command will overwrite it WITHOUT WARNING.
APPEND FROM filename [PD] [DELIMITED] [FOR <cond>]
The file in use must be open in the PRIMARY database area and the SECONDARY area must be empty i.e. it must be CLOSED. (See DISPLAY STAT for how to check whether an area is in use.) The file from which data are to be appended must not be open.
...
The PD qualifier means that if a PipeDream columnated file has been saved as Plain text, each line will be treated as a database record and read into the file.
...
The FOR <cond> option is only available when appending from another zBASE file. In this case each record in the source file is checked against the condition. If the condition evaluates to TRUE, or to a NON-ZERO value, the record will be added to the open target file.
COPY TO filename <[STRUCTURE] / [PD]>
This form of the copy command provides the opportunity to re-create the structure of the current file in another database file, or as a skeleton in PipeDream for the creation of a new file.
...
n P and into PipeDream
Load TEMP as plain text. Go to the bottom of the file and add a line
...
The new file VIDEO now contains all the records from the previous VIDEO file with an additional field called COST of type NUMERIC.
COPY TO <filename> STRUCTURE
This version of the command will create a new database file with the same structure as the current file. The new file will have no records.
Moving around a file
These commands position the record pointer to the selected record. If the record number is known, the 'GO record number' command is the fastest method of reaching a record.
SKIP
The SKIP command moves the record pointer in the direction given in the command. SKIP 3 will move the pointer on three records. SKIP -3 will move the pointer back three records.
If the end of file is reached, the EOF() function will return a non-zero value, i.e. TRUE, and the record number, RECNO() will return a 0. SKIPping past the end of file will return RECNO()=0 and EOF()=1.
GO (TO RECORD NUMBER ..) <expression>
The GO number command places the record pointer at that record number. The number must be a numeric variable or numeric expression, except when it is BOTTOM or TOP.
These commands position the pointer to the respective position at the top or bottom of the file. The record to which it is pointed is a live record and is not in front of the beginning of the file nor is it after the end. i.e. GO BOTTOM will go to the last record not to the end of file so EOF() will return FALSE.
ENVIRONMENTAL COMMANDS
-ESC- ON/OFF (v1.3 only)
The switch allows programs to ignore attempts to -ESC- and is activated by typing Set Esc=Off (deactivated by Set Esc=On) in interactive mode or by inserting it to a command line.
SET ECHO
This is a toggle command in that the first call will switch it on and the second will switch it off.
It is a programmers tool to show what command line is being executed. It is most use when debugging command files. It makes a mess of the screen but displays each command line as it is executed.
Indirect variables
&memvar
In dBASE II, these are referred to as MACROS. These & characters mean that the variable which follows the & is evaluated before being executed. In any command line from the keyboard or a command file, in which an indirect variable is found, the &variable is first replaced by the value it represents. e.g.
...
In any real program, the above would be written as GO BETA and the above is given as an example only. For a more extensive example of the use of indirect variables, see the APPEND.PRG program.
"&numericvar"
This is a particular use of the indirect variable and converts a numeric to a string.
LET numvar=42
? "&numvar"
42
? len("&numvar")
2
zBASE output to printer port
The command for this is
# "text"
or
...
See section C for a program for printing address labels.
Z88 output facilities
The copy commands explained above provide an opportunity to output to PipeDream. The method described below permits all the screen output to also go to a file or the printer.
n+ P
This sequence echoes all screen output to an attached printer. Keyboard input is double spaced at the printer.
n- P turns off this echo.
n+ S
In a similar fashion to the above printer echo system, this sequence echoes the screen output to a file. The file may be accessed via PipeDream by loading the file ram.-/s.sgn.
The switch to turn off the file echo is n - S.
System Limits
- The maximum number of records permitted in a zBASE file is 65535.
- The maximum command line length is 255.
- The maximum string variable length is 255. (Memory or field).
- Maximum number of fields per record is 32.
- Max number of nesting of IF/ENDIF loops is 255.
- Max number of nested DO WHILE's is 32
- Max number of nested DO files is 16
- Max area for memory variables is 512 bytes
- Max length of variable name is 8 characters
- Numbers are significant to 9 digits.
- Max number of decimal places is 8.
Precedence of Operators
zBASE does not consider one type of operator any more important than another. All mathematical expressions are evaluated from left to right. The only exception to this rule is that the contents of brackets are evaluated first. Programmers will quickly notice that expressions with brackets are evaluated relatively slowly, and that sorting out the expression will make the program run faster.
Using multiple files
Using multiple databases.
There are many instances in data manipulation when data from two or more databases has to be combined to achieve the desired output. zBASE supports this requirement by allowing two databases, with indices, to be open at the same time. They can then cross reference each other and find the required information without opening and closing the files.
...
There will be one record in the VIDSTAR file for each star in the film. So if the film has three stars, the VIDSTAR file will have three records, where the REF_NUM is the same as the REF_NUM of the films record in the VIDEO file, and the STAR field holds the name of one of the three stars. An example will help:
| VIDEO FILE RECORD | STARS FILE RECORDS | ||
| REF_NUM$ | 12 | REF_NUM$ | STAR$ |
| TITLE$ | Trading Places | 12 | Eddie Murphy |
| TYPE$ | COM | 12 | Dan Aykroyd |
| TAPE_NO$ | 3 | 12 | Jamie Lee Curtis |
| DURATION$ | 112 | ||
| RATING$ | 5 |
The data for the VIDSTAR file must be entered when the other details of the video are being entered. To alter the program VIDINP.PRG to do this, find the line in the program:
...
The simple subroutine below, STARINP.PRG, should then be entered using PipeDream and saved as plain text.
* STARINP.PRG V1.00 By Derek Fountain
CLS
USE VIDSTAR INDEX VIDSTAR.NDX
AT 0,28 SAY "Home video library system"
LET header$="Enter the stars who appear in "+TRIM(mtitle$)
AT 2,(80-LEN(header$))/2 SAY header$
AT 6,25 SAY "Leave the field blank to exit"
...
If the entry is not blank a new record is created in VIDSTAR. That record is filled with the unique reference number of the video, as created by VIDINP.PRG, and the stars name, as input by the user.
...
Each record of this database will contain one line of the report, which will be loading into, and printed from, PipeDream. This means three databases have to be manipulated:
| VIDEO | The main database containing details of the video. |
| VIDSTAR | + VIDSTAR.NDX. Holds details of the stars, indexed on reference number so they can be found quickly. |
| REP | Contains the lines of the report and is built up by the program. |
...
The REP file is open from start to finish in area 1, and the other two are opened and closed as necessary in area 2.
...
Copy out the file to a PipeDream file, close the database, and wait for acknowledgement that the process has finished. Then delete the work file and return.
Importing files from PipeDream
When data has been entered previously under PipeDream, it can be imported directly into zBASE using the APPEND FROM command. Assuming the PipeDream data are arranged in columns, separated by TAB characters, each line of data can be read in as a record. Each column is then a field.
The phone book from the Quick Start Guide might look like this in PipeDream. It is called PH.DAT and is stored as PLAIN TEXT.
| ................A | ..............B | ...............C | |
| 1 | Cambridge | 312216 | Sir Clive |
| 2 | Rakewell | 630617 | Vic Gerhardi |
| 3 | UserClub | 68 Well St | Roy |
| 4 | Scotland Yd | 877 1212 | Insp Bond |
...
The QSG section has a structure of
...
Fields which are too big for the database field sizes specified will be trimmed to size by lopping off the last characters.
Editing command files
Editing command files and instantly testing them is extremely simple. It can be done by using nP to go into PipeDream, and nW to return to zBASE.
Popdowns from zBASE.
Z88 popdowns may be used while in zBASE. However, the
following points should be noted.
...
Editing command files and instantly testing them is
extremely simple. It can be done by using nP to go into
Pipedream, and nW to return to zBASE.
zBASE Pocket Ref. Guide
CONVENTIONS
...
| Lowercase | operator input, usually enclosed in < > brackets. |
| UPPERCASE | specific zBASE commands or command words. |
| [....] | Optional parts of commands. |
| <...> | Operator specified input. |
| <exp>... | An expression which can result in either a number or a string. e.g. 5+5, "FRED"+"BLOGGS", a$+"MUMMY". |
| <var> ... | A variable, can mean either mvar or fvar. |
| <mvar>... | A memory variable, not stored in a database, but in a large buffer in RAM. An mvar is defined as a string if its name ends with a '$', otherwise, it is defined as a number. |
| <fvar>... | A field variable, permanently stored in a database. Fields must start with either a 1: or 2: label, depending on the database they are to be taken from. If the label is missing the field will be taken as a mvar. |
| <cond>... | A condition which returns the result either TRUE or FALSE. e.g. 10=10 is TRUE, 10=6 is FALSE, "FRED"="BLOGGS" is FALSE. A single number 0 is evaluated as FALSE, any other number is TRUE. |
...
KEYWORDS
Only the first 4 characters of a keyword are significant.
zBASE commands
| * |
| adds comments to a command file |
| ? [<exp>] |
| displays the value of an expression. |
| # [<exp>] |
| sends the value of <exp> expression through the serial port to the printer. |
| AT <co-ordinates> SAY <exp> |
| displays the value of the <exp> expression at the specified co-ordinates. |
| AT <co-ordinates> GET <var> |
| formats fields on screen for operator input. |
| APPEND BLANK |
| adds a blank record to the database in use |
| APPEND FROM <filename> [PD]/[DELIMITED] [FOR <exp>] ] |
| adds new records to the current database from another database or Pipedream file. |
| CLS |
| clears the screen. |
| CONTINUE |
| extension to LOCATE command to move to next match. |
| COPY TO <filename> [FOR <cond>] |
| creates new database from current one with optional conditional selection. |
| COPY TO <filename> [PD] {DELIMITED] [FOR<cond>] |
| copies data from current file to new format with optional conditional pull. |
| COPY TO <filename> STRUCTURE [DELIMITED] |
| creates a database file with same structure as current file, or a Pipedream file of the structure. |
| CREATE <file1> FROM <file2> |
| creates zBASE file called 'file1' from Pipedream file 'file2' of format FIELD_NAME, with $ if a string field COMMA, WIDTH if its string field. |
| DELETE RECORD |
| marks current record for deletion. |
| DELETE FILE |
| removes selected file from directory. |
| DISPLAY<[STRUCTURE]/[MEMORY]/[STATUS]> |
| shows on screen the selected option related to current use of database, memory variables and files respectively. |
| DISPLAY <[ALL] / [FOR <cond>]> <[FIELDS field,field,field]> |
| shows data from current file in use [ALL] - shows seven records before pausing. |
| DO <command file> |
| runs a command file. |
| DO WHILE <cond> - ENDDO |
| runs the commands enlosed in loop as long as <cond> is TRUE. |
| FIND <exp> |
| searches fo key field match in indexed file. |
| GO [<exp> / <BOTTOM> / <TOP>] |
| moves record pointer to <exp>th record or top/bottom. |
| IF <cond> - ELSE - ENDIF |
| runs the commands after IF if <cond> is TRUE, otherwise runs commands after ELSE. |
| INDEX ON <fvar> TO <filename> |
| creates an index file in order of fvar. |
| LET <var>=<exp> |
| establishes a value for a variable. |
| LIST [ALL] |
| works as DISPLAY without the pause every 8 lines. [ALL] - shows all records without pausing. |
| LOCATE FOR <cond> |
| moves record pointer to first record in file for which <cond> is TRUE. |
| QUIT |
| closes all files and zBASE application. |
| RECALL RECORD |
| removes DELETE mark on a record |
| RELEASE <mvar> |
| removes specified memory variables. |
| RENAME <file1> TO <file2> |
| changes name of file. |
| RETURN |
| stops running current command file and returns control to previous command file or curly prompt. |
| SELECT <[1 or 2]> |
| opens selected database area. |
| SKIP [<exp>] |
| moves record pointer <exp> records along. |
| USE [<file>] |
| closes current file and opens <file> if specified. |
| USE file INDEX file |
| opens database in current area with index file. |
| WAIT |
| pauses operation until a key is pressed. |
zBASE Functions
| CHR(<exp>) | returns charater with ASCIIcode exp. |
| CLI (<exp$) | sends <exp$> to the OZ CLI function for immediate execution. |
| DATE() | provides current system date. |
| DELETED() | returns 1 or 0 (TRUE / FALSE) to reflect status of current record. |
| EOF() | returns 1 or 0 if end of file has been reached or not respectively. |
| FILE(<exp$>) | responds with TRUE if file defined by exp does exist. |
| INT(<exp>) | returns integer from exp. |
| LEN(<exp$>) | shows length of string variable specified. |
| LOWER(<exp$>) | turns string into lower case. |
| LTRIM(<exp$>) | removes left hand blanks in string exp. |
| RAM() | reveals RAM space available on currently selected device. |
| RECNO() | returns current record number. |
| SET ECHO | toggles echoing of all commands to screen. |
| STR | To emulate a STR function use &. } LET A=2.03 } LET A$="&A" } ? "-"+a$+"-" -2.03- |
| SUBSTR(<exp1$>, <exp2>,<exp3>) | extracts the sub-string from exp1$ defined as starting at position exp2, of length exp3. |
| TIME() | displays system time. |
| TRIM(<exp$>) | removes trailing blanks. |
| UPPER(<exp$>) | converts string exp$ to upper case. |
| VAL(<exp$>) | converts ASCII string to its numeric equivalnet. |
| WHERE(<exp1$>, <exp2$>) | shows the starting character position for where exp1$ occurs in exp2$. |
...
zBASE Commands
Most of the zBASE commands may be used both in the interactive mode at the curly prompt, or in program files or command files. The main exceptions to this rule are that related pairs of commands such as IF/ENDIF and DO WHILE/ENDDO may not be used in the interactive mode.
...
At present only a single condition is allowed. i.e. there are no AND, OR or NOT clauses.
KEYWORDS
Only the first 4 characters of a keyword are significant.
* Comments
Any line beginning with an * will be ignored. This can be used as a method of putting comments in command files. e.g.
}* This is a comment line and will be ignored
}
? [<exp>]
This command shows the value of an expression. The result is printed at the current cursor position, with no CR or LF following.
...
}? "Hello world"
Hello world
}? 10+10
20
}? 1:phone$
01296 43 78 78
# [<exp>]
This command works just like the ? command, only the expression is sent out of the serial port, instead of to the screen.
AT <co-ordinates> SAY <exp>
This command prints the value of the expression at the specified co-ordinates. The co-ordinates are taken as 'down' (0-7) then 'across' (0-79). A string will be printed in full, including trailing spaces and a number will be printed to 9 significant digits and up to 8 decimal places. e.g.
}AT 3,40 SAY "Merry Christmas"
Merry Christmas
AT <co-ordinates> GET <var>
This command allows the input of a variable, either field or memory variable. The co-ordinates are taken as for AT SAY with the variable then being offered up at the specified co-ordinates for editing. The variable must exist prior to the issuing of the GET command.
...
LET mvar$="0101 212 800 5555"
AT 3,30 GET mvar$
APPEND [BLANK] / [FROM <filename> [PD]/[DELIMITED] [FOR <exp>] ]>
This command is used to add new records to the currently selected database.
...
The PD clause means the fields are separated by TAB (09h) characters and the records are separated by CR (0Dh) characters.
The command line is
APPEND FROM [filename] PD
The file shown below, having been saved as PLAIN TEXT, will then be appended onto the end of the database.
...
| ................A | ..............B | ...............C | |
| 1 | Cambridge | 312216 | Sir Clive |
| 2 | Rakewell | 630617 | Vic Gerhardi |
| 3 | UserClub | 68 Well St | Roy |
| 4 | Scotland Yd | 877 1212 | Insp Bond |
The DELIMITED clause means the fields are separated by commas and the records by CR (0Dh) LF (0Ah). This is a common format output by dBase and many spreadsheets.
...
The following file would be appended to the database in use.
...
| ................A | ..............B | ...............C | |
| 1 | Cambridge,312216,Sir Clive | ||
| 2 | Rakewell,630617,Vic Gerhardi | ||
| 3 | UserClub,68 Well St,Roy | ||
| 4 | Scotland Yd,877 1212,Insp Bond | ||
...
If the PD and DELIMITED instructions are omitted the file is assumed to be a zBASE file.
CLS
This command clears the screen.
CONTINUE
This command locates the next record which matches the condition specified in the last LOCATE command.
...
The CONTINUE command is not designed for use with the FIND command. If CONTINUE is used after a FIND it is only coincidence if matching records are found.
COPY TO <filename> [PD] [DELIMITED] [FOR <cond>]
The copy command is the method of outputting data to another format. If none of the options are specified the output file will be another zBASE file.
If PD is specified the data will be written out in a format which PipeDream can read in plain text mode.
e.g. COPY TO <filename> PD
If DELIMITED is specified the data will be written out in a comma delimited format which can be read in by dBase or a Spreadsheet package. e.g.
COPY TO <filename> DELIMITED
If the FOR clause is specified only those records which meet <cond> will be copied to the output file. e.g.
...
copies the same set of records but this time the output is in PipeDream format. Similarly, the use of DELIMITED would out to a comma delimited file.
COPY TO <filename> [STRUCTURE] [DELIMITED]
This second version of the COPY command provides two alternative outputs.
...
COPY TO <filename> STRUCTURE DELI, creates a PipeDream file of the form required to create a new zBASE file. The new file created from such a file would have the same structure as the original database from which the structure was taken.
CREATE <file1> FROM <file2>
This version of the CREATE command creates a database file called 'file1' from an input file, 'file2' which is created under PipeDream. The format for file2 must follow these rules:
- One line per field in database.
- No blank lines, and no extra CR at the end of the last field.
- All string field names end in $, followed by a comma and a number indicating the length of the field (1-255).
- Numeric fields have just the name on the line, nothing else.
e.g.
| NAME$,25 | NAME is a string field, length 25 |
| AGE | AGE is a numeric field |
| SCORE$,10<END> | SCORE is a string field, length 10 |
Any stray CRs, or text in the wrong place may cause strange results.
The database file created will be left open in the selected database area. If the CREATE fails for any reason, the selected area is left empty.
DELETE <[RECORD] / [FILE <filename>] >
The DELETE RECORD command marks the current record for deletion. The record is not actually removed from the file. When the record is DISPLAYed a '*' will appear next to the first field indicating the record is marked for deletion.
To actually remove deleted records from the database, see the program PACK.PRG.
DELETE FILE filename will erase the file from the Z88's Ramdisk. If it doesn't exist, an error message will appear.
DISPLAY/LIST <[STRUCTURE]/[MEMORY]/[STATUS]>/
<[ALL]/[FOR <cond>]> <[FIELDS field list]>
The display commands can be called using the LIST keyword. The only difference in their operation is that DISPLAY pauses for each screenfull of data, and LIST doesn't.
...
If the MEMORY clause if used, the memory variables and their values are listed on screen. e.g.
| address1$ | STRING | "54 Moor Road" |
| address2$ | STRING | "Linstanton" |
If the STATUS clause is used the machines current status is displayed on screen.
...
Note that the 1: is not required for the list of field names.
DO <command file>
This command executes the specified command file. All commands in the file are in standard zBASE syntax. Control is passed back to the keyboard when the last instruction has been executed, or a RETURN is encountered.
DO WHILE <cond> - ENDDO
The DO WHILE command can only be executed from within a command file. The condition is evaluated, and, if it is TRUE the statements following the DO are executed until an ENDDO is found. At that point control is passed back up to the DO and the condition is re-evaluated.
...
Also note the expression 'DO WHILE 1' would put the machine into an infinite loop.
FIND <exp>
Find searches the current index file for the value <exp>. It is zBASE's quickest method of finding data, searching some 4000 bytes per second. The only field it scans is the index key field. e.g.
}USE TEST
}INDEX ON NAME$ TO TESTNAME.NDX
}FIND "Derek Fountain"
}DISPLAY
465 Derek Fountain Aylesbury
}FIND "Aylesbury"
}DISPLAY
0
}INDEX ON TOWN$ TO TEST.NDX
}FIND "Aylesbury"
}DISPLAY
465 Derek Fountain Aylesbury
GO [<exp>/<BOTTOM>/<TOP>]
The GO command positions the current record pointer at an absolute record number, specified by exp. Trying to move to a number less than 1 will place the record pointer at 1, and trying to move to a record number which doesn't exist will place the record pointer at the last record in the file (not EOF).
...
} ? RECNO()
24
} GO 10
} ? RECNO()
10
} LET a=30
} GO a
} ? RECNO()
30
} GO BOTTOM
} ? RECNO()
98
} GO TOP
} ? RECNO()
1
IF <cond> - ELSE - ENDIF
The IF command allows conditional execution of statements from within a command file, but without the looping system the DO WHILE statement uses.
...
In the second example, if a$ is the same as b$ then 'Its equal' will be printed, followed by 'Goodbye'. If a$ is not the same as b$, then 'Its not equal' will be printed, followed by 'Goodbye'.
INDEX ON <fvar> TO <filename>
Index is zBASEs method of sorting a database, and keeping it sorted. When a database is indexed on a field, any records that are appended to it automatically take up their correct place in the file. If the file is USEd without the index file, the records go back to chronological order. E.g.
}USE TEST
}LIST ALL
1 Fred
2 Bob
3 Peter
}INDEX ON NAME$ TO TEST.NDX
}GO TOP
}LIST ALL
1 Bob
2 Fred
3 Peter
}APPEND BLANK
}LET 1:NAME$="Derek"
}GO TOP
}LIST ALL
1 Bob
2 Derek
3 Fred
4 Peter
}USE TEST
}LIST ALL
1 Fred
2 Bob
3 Peter
4 Derek
LET <var>=<exp>
The LET command assigns a value to a specified variable. In the generic case, the value to be allocated to the variable is the value of the expression <exp>. The label to be given to the variable is the name contained in the space <var>. e.g.
LET today$=date()
LET spaces$=" "
LET codename$="Fred"
LOCATE FOR <cond>
The locate command is used for finding a record which meets a specified condition. The record pointer will be moved to the top of the file and each record checked to see if <cond> is true. If it isn't the next record is checked and so on until the EOF is found or a record meets the condition. The record pointer will be left pointing to the correct record, or EOF if there wasn't one. e.g.
} ? RECNO()
24
} LOCATE FOR 1:NAME$="Fred"
} ? RECNO()
14
} LOCATE FOR 1:NAME$="Gertrude"
} ? EOF()
1
QUIT
This command closes all open files, and returns the Z88 back to its main applications menu.
RECALL RECORD
This command performs the opposite of the delete command. A record marked for deletion will be 'unmarked'. If the record wasn't deleted, the command is ignored.
RELEASE <mvar>
When a memory variable has served its purpose and is no longer needed, it can be removed from RAM to free space. e.g.
} RELEASE name$
} ? name$
Variable not found
RENAME <file1> TO <file2>
This command renames file1 to file2 in the same way the option from the Filer does. If file2 exists or file1 doesn't an error message will appear. Note you can't rename a file which is open.
RETURN
Return halts the execution of the current command file and returns control back to the curly prompt or the calling file.
All files are left open and memory variables are maintained.
SELECT <[1 or 2]>
zBASE can have two databases open at the same time, for cross referencing purposes. This command selects between the two database areas and defines which database will be used for DISPLAY commands, and which area a new database will be opened in when a USE command is issued.
The two areas are called PRIMARY and SECONDARY or simply 1 and 2. Only the 1 or 2 may be used in the actual command.
SKIP [<exp>]
The skip command moves the current record pointer. If <exp> is specified it must be a number. The record pointer will move that number of records through the file, from its current position. A negative number will make it move backwards. Trying to move past the beginning of the file will leave the record pointer at record 1, and trying to move past the end of the file will set EOF true.
...
} ? RECNO()
24
} SKIP
} ? RECNO()
25
} SKIP 10
} ? RECNO()
35
} SKIP -4
} ? RECNO()
31
USE [<file>]
This command opens a new database in the currently selected area. If the filename is not specified the database currently open is closed and the area left empty. Only files created with the CREATE command can be opened using USE. i.e. only zBASE files.
The alternative form opens an associated INDEX file viz:
USE file INDEX file
WAIT
This command simply pauses the system until a key is pressed. When used in a command file it is useful to display a 'WAITING' message so that the operator knows that a key is awaited.
If this is done, the 'WAITING' message should be erased after a key press.
zBASE Functions
zBASE supports all the standard functions found in other languages plus some specialised database handling ones of its own.
...
} LET A=2.03
} LET A$="&A"
} ? "-"+a$+"-"
-2.03-
CHR(<exp>)
The CHR function returns a single character string containing the character whose ASCII code is <exp>. e.g.
} ? CHR(65)
A
} ? CHR(124)
|
CLI (<exp$)
The CLI function sends <exp$> to the OZ CLI function for immediate execution.
DATE()
The date function returns the current date as an eight bit string. The date is taken from OZ, and is returned in the system default format i.e. European or American as set by the panel. e.g.
} ? DATE()
18/08/88
DELETED()
The DELETED function returns a 1 (TRUE) or a 0 (FALSE) depending on whether the current record is marked for deletion or not. e.g.
} DELETE RECORD
} ? DELETED() 1
} RECALL RECORD
} ? DELETED()
0
EOF()
The EOF (End of file) function returns a 1 (TRUE) or a 0 (FALSE) depending on whether the current file record pointer is at end of file or not. e.g.
} GO BOTTOM
} ? EOF()
0
} SKIP
} ? EOF()
1
FILE(<exp$>)
The FILE function returns a 1 (TRUE) or a 0 (FALSE) depending on whether the file <exp$> exists or not. Note that <exp$> is an expression and not a literal. e.g.
} ? FILE("NAMES.DBF")
1
} USE NAMES.DBF
INT(<exp>)
The INT (Integer) function removes all digits from the number <exp> which follow the decimal point. e.g.
} ? INT(3.142)
3
} ? INT(200.000)
200
} ? INT(22/7)
3
LEN(<exp$>)
The LEN function returns the length of string expression <exp>. e.g.
} ? LEN("HELLO WORLD")
11
} LET A$="FOO BAR ZOK POW"
} ? LEN(A$)
15
LOWER(<exp$>)
The LOWER function turns all the characters in the string <exp> into lower case. Any characters that were already in lower case will be left alone. e.g.
} ? LOWER("Fred Bloggs")
fred bloggs
LTRIM(<exp$>)
The LTRIM function removes all leading spaces from the string expression <exp>. e.g.
} ? "1"+LTRIM(" 2345")+"6"
123456
RAM()
reveals RAM space available on currently selected device.
RECNO()
The RECNO function returns the current file current record number. e.g.
} GO 10
} ? RECNO()
10
} GO BOTTOM
} ? RECNO()
98
} SKIP
} ? RECNO()
0
SET ECHO
toggles echoing of all commands to screen.
STR
To emulate a STR function use &.
} LET A=2.03
} LET A$="&A"
} ? "-"+a$+"-"
-2.03-
SUBSTR(<exp1$>,<exp2>,<exp3>)
The SUBSTR (Substring) function returns that part of <exp1$> that starts at <exp2> and is <exp3> characters long. Examples make this clearer:
...
Note that if <exp2>+<exp3> > LEN(<exp1$>) no error occurs.
TIME()
The time function returns an eight character string holding the current time in the format HH:MM:SS. The time is fetched from OZ and can be altered using nT. e.g.
...
To obtain time differences, sub strings of the time string will have to be extracted and converted to numbers using the VAL() function.
TRIM(<exp$>)
The TRIM function removes the trailing spaces from the end of string <exp>. e.g.
} ? "1"+TRIM("2345 ")+"6"
123456
UPPER(<exp$>)
The UPPER function turns all the characters in the string <exp> into upper case. Any characters that were already in upper case will be left alone. e.g.
} ? UPPER("Fred Bloggs")
FRED BLOGGS
VAL(<exp$>)
The VAL function turns an ASCII string into its numeric equivalent. Conversion stops at the first non ASCII digit character. e.g.
} ? VAL("123")
123
} ? VAL("10")+10
20
WHERE(<exp1$>,<exp2$>)
The where function returns the position of <exp1$> in <exp2$>. If it is not present, 0 is returned. e.g.
} ? WHERE("23","1234")
2
} ? WHERE("HELLO",UPPER("hello world"))
1
} ? WHERE("78","1234")
0
zBASE Programs
The programs listed in this manual are designed to be indications only of the potential of zBASE. They are for users to amend to suit their own purposes and are not intended as complete solutions. They have not been exhaustively tested.
...
Those who wish to type in the programs by hand, be warned that some code lines have spaces in them which are not normally seen in these listings. The space character has been replaced by øunless the spaces are in a comment line. Take care that you count the number of spaces correctly.
These programs are in programs.doc which you can now download from this site.
...
They may also be obtained on a PC disk for £5, plus VAT, direct from Rakewell.
Sample programs
These files may be copied and adapted by owners of a zBASE licence at no charge.
Wordmongers retains all copyright in them.
...
...
...
| MAIN.PRG | A menu program for database management |
| NEWUN.PRG | Called by MAIN to enter new records. |
| APPEND.PRG | A command file to make data entry easier. |
| APPEND.DEF | A database structure file for use by the APPEND program. |
| PACK.PRG | To remove deleted records from a file |
| PHENT.PRG | Phone book entry program |
| FPROG | Find program for phone book |
| VIDINP.PRG | Input routine for VIDEO file |
| STARINP.PRG | Input for stars in Videos |
| VIDREP.PRG | Report generator for video system |
| VIDREP.DEF | USE REP.DEF FROM STOCK CONTROL SYSTEM |
| Stock Check suite. | See introduction page for this suite. |
MAIN.PRG
* MAIN.PRG - A menu program for database file * management.
* TITLE.PRG
doøwhileø1=1
øcls
øatø2,10øsayø"TheøWordmongersøzBASEøAddressøbook.øByøCøSalvidge."
øatø3,15øsayø"(c)øWordmongersøLtdø1988."
øatø5,10øsayø"(S)earchøforøanøentry.ø(E)nterønewøperson.ø(Q)uit."ø
øatø7,10øsayø"Yourøchoiceøplease"
øletøchoice$="ø"
ødoøwhileøwhere(choice$,"SEQ")=0
øøatø7,30øgetøchoice$
øøletøchoice$=upper(choice$)
øenddo
øiføchoice$="Q"
øøreturn
øendif
øiføchoice$="S"
øødoøfindum.prg
øendif
øiføchoice$="E"
øødoønewun.prg
øendif
enddo
NEWUN.PRG
* NEWUN.PRG - Called by MAIN to enter new records.
cls
at1,0say"Title:øøøøøøForename:øøøøøøøøøøSurname:"
atø3,0sayø"Enterøtheønameøoføtheøpersonøtoøaddø"øatø4,0øsayø"Leaveøalløtheøfieldsøblankøtoøcancel"
letøtitle$="øøø"
letøforname$="øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
letøsurname$="øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
atø1,5øgetøtitle$
atø1,20øgetøforname$
atø1,52øgetøsurname$
ifølen(surname$)=0
øifølen(forname$)=0
øøifølen(title$)=0
øøøøcls
øøøø?ø"CancelledøHitøanyøkey"
øøøøwait
øøøøreturn
øøendif
øendif
endif
letøusurnam$=upper(surname$)
letøufornam$=upper(forname$)
letølooking$="Y"
locateøforøupper(1:surname$)=usurnam$
iføeof()=1
øøletølooking$="N"
endif
goøtop
doøwhileølooking$="Y"
øøcontinue
øøiføeof()ø<>ø1
øøøøiføupper(1:forname$)ø=øufornam$
øøøøøøcls
øøøøøø?ø"Thatøpersonøisøalreadyøonøtheødatabase-Tryøagain"
øøøøøø?ø"Pressøanyøkeyøtoøcancel"
øøøøøøwait
øøøøøøreturn
øøøøendif
øøøøiføupper(1:forname$)ø<>øufornam$
øøøøølooking$="N"
øøøøendif
øøendif
øøiføeof()ø=ø1
øøøøletølooking$="N"
øøendif
enddo
appendøblank
letø1:surname$=surname$
letø1:forname$=forname$
letø1:title$=title$
atø2,0øsayø"Addressøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
atø4,0øsayø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
atø3,0øsayø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
atø5,0øsayø"Note"
atø2,10øgetø1:add1$
atø3,10øgetø1:add2$
atø4,10øgetø1:add3$
atø5,10øgetø1:note$
return
APPEND.PRG
* APPEND.PRG - A command file to make data entry easier.
*ø************************************
* APPEND.PRG Will append new records *
* to the database that is open in 1: *
*ø************************************
*
* The database to be appended to is open in 1
* First copy its structure out to a PD file
selectø1
copyøtoøtemp.deføstructureøPD
selectø2
* Now, in 2, Create a database for the structure to be read in to
create st.dbf from append.def
* Read in the structure
appendøfromøtemp.deføPD
useøst.dbf
letødoing=1
doøwhileødoing=1
øselectø1
øappendøblank
øcls
øatø0,0øsayø"Recordønumberø-ø"
øatø0,16øsayørecno()
øselectø2
øgoøtop
ødoøwhileøeof()=0
øøselectø2
øøatø7,0øsayø2:field$
øøletøf$="1:"+2:field$
øøatø7,10øgetø&f$
øøskip
øø?
øenddo
øletøchoice$="ø"
ødoøwhileøwhere(choice$,"YN")=0
øøøatø7,0øsayø"Addøanotherørecordø?øY/N"
øøøatø7,25øgetøchoice$
øøøletøchoice$=upper(choice$)
øenddo
øiføchoice$="N"ø
øøøletødoing=0
øendif
enddo
* Now clean up
selectø2
use
deleteøfileøst.dbf
selectø1
* Thats it folks
APPEND.DEF
* APPEND.DEF - A database structure file for use by the
* APPEND program.
* Do not enter the * lines to the append.def file in Pipedream.
field$,10
type$,3
PACK.PRG
* PACK.PRG Removes deleted records from file.
CLS
IFøFILE(TEMP)
øøATø2,15øSAYø"FileøcalledøTEMPøcurrentlyøexists."
øøATø3,15øSAYø"Pleaseøremoveøit.øøPACKøneedsøthatø"
øøATø4,15øSAYø"fileønameøasøaøtemporaryøworkøfile."
øøATø7,15øSAYø"Pressøanyøkeyøtoøreturnøtoø}."
øøWAIT
øøRETURN
ENDIF
USE
LETøSPACE40$="øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
LETøNEWFILE$=SUBSTR(SPACE40$,1,12)
ATø2,15øSAYø"Enterønameøoføfileøtoøbeøpacked.."
ATø2,50øGETøNEWFILE$
ATø4,15øSAYø"Renamingø"+NEWFILE$+"øtoøTEMP."
RENAMEø&NEWFILE$øTOøTEMP
USEøTEMP
COPYøTOø&NEWFILE$øFORøDELETED()=0
USE
DELETEøFILEøTEMP
RELEASEøNEWFILE$,øSPACE40$
RETURN
* EOF
PHENT.PRG
* PHENT.PRG
LETødoing=1
* following line sets up variable of 20 spaces
LETøSPACE20$="øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
DOøWHILEødoing=1
øøLETøCOMP$=SUBSTR(SPACE20$,1,15)
øøLETøPHONE$=SUBSTR(SPACE20$,1,17)
øøLETøNAME$=SPACE20$
øøLETøKEYFIELD$=SUBSTR(SPACE20$,1,5)
øøCLS
øøATø0,10øSAYø"ENTERøCompanyøname..."
øøATø1,10øSAYø"ENTERøcontactøname..."
øøATø2,10øSAYø"ENTERøphoneønumber..."
øøATø3,10øSAYø"ENTERøKEYFIELDøVALUE."
øøATø0,33øGETøCOMP$
øøATø1,33øGETøNAME$
øøATø2,33øGETøPHONE$
øøIFøCOMP$="ø"
øøøøLETøKEYFIELD$=SUBSTR(NAME$,1,5)
øøELSE
øøøøLETøKEYFIELD$=SUBSTR(COMP$,1,5)
øøENDIF
øøATø3,33øGETøKEYFIELD$
øøLETøconfirm$="N"
øøATø5,10øSAYø"Confirmøthisørecordøtoøbeøaddedøtoøfile.øY/N."
øøATø5,57øGETøconfirm$
øøIFøconfirm$="Y"
øøøøAPPENDøBLANK
øøøøLETø1:COMP$=COMP$
øøøøLETø1:NAME$=NAME$
øøøøLETø1:PHONE$=PHONE$
øøøøLETø1:KEYFIELD$=KEYFIELD$
øøELSE
øøøøATø5,57øSAYø"NOTøAPPENDED"
øøENDIF
øøLETøchoice$="ø"
øøDOøWHILEøWHERE(choice$,"YN")=0
øøøøATø7,10øSAYø"Addøanotherørecord?øY/N"
øøøøATø7,35øGETøchoice$
øøøøLETøchoice$=UPPER(choice$)
øøENDDO
øøIFøchoice$="N"
øøøøLETødoing=0
øøENDIF
ENDDO
RELEASEødoing,øSPACE20$,øCOMP$,øNAME$,øPHONE$,KEYFIELD$
RELEASEøchoice$,øconfirm$
RETURN
* END OF COMMAND FILE
FPROG
* FPROG - Programmed FIND routine for phone book
letøSPACE20$="øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
LETømseek$=SUBSTR(SPACE20$,1,5)
LETølooping=1
DOøWHILEølooping
øøcls
øøATø1,10øSAYø"Findøwhat??"
øøATø1,38øGETømseek$
øøLETømseek$=TRIM(mseek$)
øøIFøLEN(mseek$)=0
øøøøLETømseek$="ø"
øøENDIF
øøATø2,ø0øSAYø"ø"
øøIFømseek$="ø"
øøøøLETølooping=0
øøELSE
øøøøFINDømseek$
øøøøIFøEOF()=1
øøøøøøATø2,10øSAYø"Noøfind"
øøøøELSE
øøøøøøDISP
øøøøENDIF
øøøøATø7,10øSAYø"WAITING"
øøøøWAIT
øøøøATø7,10øSAYø"øøøøøøø"
øøENDIF
ENDDO
DISP
RELEASEøSPACE20$,øMSEEK$
RETURN
* EOF
VIDINP.PRG
* VIDINP.PRG V1.00 By Derek Fountain
CLS
USEøVIDEO
GOøBOTTOM
LETønref_num=VAL(1:REF_NUM$)
ATø0,28øSAYø"Homeøvideoølibraryøsystem"
ATø2,51øSAYø"Tapeøø:"
ATø4,16øSAYø"Titleø:"
ATø4,51øSAYø"Typeøø:"ø
ATø5,16øSAYø"Length:"
ATø5,51øSAYø"Rating:"
DOøWHILEø1=1
øøLETønref_num=nref_num+1
øøLETømref_num$="&nref_num"
øøLETømtape_no$="øøø"
øøLETømtitle$="øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
øøLETømtype$="øøø"
øøLETømduration$="øøø"
øøLETømrating$="ø"
øøATø2,16øSAYø"Refønumber:ø"+mref_num$
øøATø2,58øSAYømtape_no$
øøATø4,23øSAYømtitle$
øøATø4,58øSAYømtype$
øøATø5,23øSAYømduration$
øøATø5,58øSAYømrating$
øøATø7,23øSAYø"Enterøtheøinformationøonøtheøvideo"
øøATø2,58øGETømtape_no$
øøIFømtape_no$="øøø"
øøøøRELEASEønref_num,mref_num$,mtape_no$,mtitle$,mtype$,mduration$
øøøRELEASEømrating$,confirm$
øøøøRETURN
øøENDIF
øøATø4,23øGETømtitle$
øøATø4,58øGETømtype$
øøATø5,23øGETømduration$
øøATø5,58øGETømrating$
øøLETøconfirm$="ø"
øøDOøWHILEøconfirm$="ø"
øøøøATø7,23øSAYø"Pleaseøconfirmøthisøinformation:ø"
øøøøATø7,56øGETøconfirm$
øøøøIFøWHERE(confirm$,"YNyn")=0
øøøøøøLETøconfirm$="ø"
øøøøENDIF
øøENDDO
øøIFøUPPER(confirm$)="Y"
øøøøAPPENDøBLANK
øøøøLETø1:REF_NUM$=mref_num$
øøøøLETø1:TAPE_NO$=mtape_no$
øøøøLETø1:TITLE$=mtitle$
øøøøLETø1:TYPE$=mtype$
øøøøLETø1:DURATION$=mduration$
øøøøLETø1:RATING$=mrating$
øøøø*øFLAGøA
øøELSE
øøøøLETønref_num=nref_num-1
øøENDIF
ENDDO
STARINP.PRG
* STARINP.PRG V1.00 By Derek Fountain
CLS
USEøVIDSTARøINDEXøVIDSTAR.NDX
ATø0,28øSAYø"Homeøvideoølibraryøsystem"
LETøheader$="Enterøtheøstarsøwhoøappearøinø"+TRIM(mtitle$)
ATø2,(80-LEN(header$))/2øSAYøheader$
ATø6,25øSAYø"Leaveøtheøfieldøblankøtoøexit"
DOøWHILEø1=1
øøLETømstar$="øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
øøATø4,30øGETømstar$
øøIFømstar$="øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"øøøøUSEøVIDEO
øøøøCLS
øøøøRELEASEømstar$,header$
øøøøRETURN
øøENDIF
øøATø4,25øSAYø"Creatingørecordø-øPleaseøwait"
øøAPPENDøBLANK
øøLETø1:REF_NUM$=mref_num$
øøLETø1:STAR$=mstar$
øøATø4,25øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
ENDDO
* EOF
VIDREP.DEF
* VIDREP.DEF
LINE$,100
VIDREP.PRG
* VIDREP.PRG V1.00 By Derek Fountain
CLS
SELECTø1
CREATEøREPøFROMøREP.DEF
APPENDøBLANK
LETø1:LINE$="TAPEøTITLE/STARRINGøøøøøøøTYPEøDURATIONøRATING"
SELECTø2
USEøVIDEO
ATø0,28øSAYø"Homeøvideoølibraryøsystem"
LETøfilename$="øøøøøøøøøø"
ATø2,20øSAYø"Pleaseøenterøtheønameøforøtheøreportøfile"
ATø6,25øSAYø"Leaveøtheønameøblankøtoøabandon"
ATø4,35øGETøfilename$
IFøfilename$="øøøøøøøøøø"
øøUSE
øøSELECTø1
øøUSE
øøDELETEøFILEøREP
øøRELEASEøfilename$
øøRETURN
ENDIF
CLS
ATø0,28øSAYø"Homeøvideoølibraryøsystem"
ATø3,25øSAYø"Creatingøworkfileø-øPleaseøwait"
DOøWHILEøEOF()=0
øøSELECTø1
øøAPPENDøBLANK
øøSELECTø2
* following must be typed on one line
øøLETø1:LINE$="ø"+2:TAPE_NO$+"ø"+2:TITLE$+"ø"+2:TYPE$"øøøø"+2:DURATION$+"øøøøøøø"+2:RATING$
øøLETøkey$=2:REF_NUM$
øøLETøloc=RECNO()
øøUSEøVIDSTARøINDEXøVIDSTAR.NDX
øøFINDøkey$
øøDOøWHILEø2:REF_NUM$=key$
øøøøSELECTø1
øøøøAPPENDøBLANK
øøøøSELECTø2
øøøøLETø1:LINE$="øøøøø"+2:STAR$
øøøøSKIP
øøENDDO
øøSELECTø1
øøAPPENDøBLANK
øøSELECTø2
øøUSEøVIDEO
øøGOøloc
øøSKIP
ENDDO
ATø3,23øSAYø"Creatingøreportøfileø-øPleaseøwait"
USE
SELECTø1
GOøTOP
COPYøTOø&filename$øPD
USE
ATø3,23øSAYø"Reportøfileøcreatedø-øPressøanyøkey"
WAIT
DELETEøFILEøREP
RETURN
* EOF
Wordmongers Stock Control System
This suite was written to demonstrate zBASE' ability to run fully menu driven suites. It was designed with a small shop in mind, where the manager would go round his warehouse, with his Z88 and take a check of all the items he has in stock. The system would then produce a report giving details of how many of product X was in stock and how much it was all worth.
...
Option 4 produces a Pipedream plain text file, including all details held in the products file.
...
Option 5 produces a Pipedream plain text file, including all details held in the suppliers file.
...
Here is a list of the files required to run the system. The files can be obtained by sending a blank 32k eprom to us or downloading the zip file.
| File Name | Bytes | Description |
| REP.DEF | 128 | Definition of file used in stock report |
| SCFETCH.EXE | 512 | CLI File to extract these files from EPROM |
| SCOUTPRO.PRG | 1280 | Outputs the Product file in PD format |
| SCOUTSUP.PRG | 1280 | Outputs the Supplier file in PD format |
| SCPACK.PRG | 768 | Cleans, Packs & Reindexs the Databases |
| SCPROD | 384 | The Product database |
| SCPROD.DEF | 128 | The Definition of the Product database |
| SCPROD.NDX | 128 | The index for the Product database |
| SCSIAM.PRG | 1408 | Amend Product |
| SCSIBACK.PRG | 640 | Skip back one product |
| SCSIDELE.PRG | 512 | Delete a product |
| SCSIFIND.PRG | 640 | Find a product |
| SCSIINP.PRG | 1920 | Input a product |
| SCSIMAIN.PRG | 2176 | Products file maintenance menu |
| SCSINEXT.PRG | 384 | Skip forward a product |
| SCSIRECA.PRG | 512 | Recall a deleted product |
| SCSTART.PRG | 1152 | The main menu |
| SCSTKREP.PRG | 2944 | The stock report |
| SCSTOCK.PRG | 1920 | Amend stock numbers |
| SCSUAM.PRG | 1408 | Amend suppliers |
| SCSUFIND.PRG | 768 | Find a supplier |
| SCSUINP.PRG | 2048 | Input a supplier |
| SCSUMAIN.PRG | 2432 | Suppliers file maintenance menu |
| SCSUPP | 384 | The Suppliers Database |
| SCSUPP.NDX | 128 | The index file for the supplier file |
| SCSUPP.DEF | 128 | The definition of the supplier file |
| ZBDEMO.DOC | 4400 | This file |
| ZBRUN | 256 | The Autoexec file |
REP.DEF
* REP.DEF
LINES,115
SCOUTSUP.PRG
* SCOUTSUP.PRG V1.01 BY DEREK FOUNTAIN
* OUTPUT SUPPLIERS FILE TO A PD FILE
DOøWHILEø1=1
øøCLS
øøATø0,30øSAYø"OUTPUTøSUPPLIERøFILE"
øøATø2,20øSAYø"Pleaseøenterøtheønameøoføtheøoutputøfile"
øøLETøfilenam$="øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
øøATø6,25øSAYø"Leaveøtheønameøblankøtoøabandon"
øøATø4,30øGETøfilenam$øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø
øøIFøfilenam$="ø"
øøøøRELEASEøfilenam$,over$
øøøøRETURN
øøENDIF
øøATø2,20øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
øøATø4,30øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
øøATø6,25øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
øøLETøover$="Y"
øøIFøFILE(filenam$)=1
øøøøATø3,20øSAYø"Fileøexistsø-øOverwriteøit?ø(Y/N)ø>>>"
øøøøLETøover$="ø"
øøøøDOøWHILEøover$="ø"
øøøøøøATø3,59øGETøover$
øøøøøøIFøWHERE(over$,"YyNn")=0
øøøøøøøøLETøover$="ø"
øøøøøøENDIF
øøøøENDDO
øøENDIF
øøIFøUPPER(over$)="Y"
øøøøATø3,20øSAYø"CopyingødataøtoøPipedreamøfileø"+filenam$
øøøøUSEøSCSUPP
øøøøCOPYøTOø&filenam$øPD
øøøøATø3,20øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
øøøøATø3,11øSAYø"Processøcompletedø-øTheøfileøMUSTøbeøloadedøasøplainøtext"
øøøøATø5,27øSAYø"Pressøanyøkeyøtoøcontinue"
øøøøWAIT
øøøøRELEASEøfilenam$,over$
øøøøRETURN
øøENDIF
ENDDO
SCPACK.PRG
* SCPACK.PRG V1.02 BY DEREK FOUNTAIN
* Same as a dBase pack - it removes the deleted record
CLS
ATø0,30øSAYø"CLEANøFILESøROUTINE"
ATø3,19øSAYø"Removingødeletedørecordsømayøtakeøsomeøtime"
ATø5,20øSAYø"Confirmøyouøwantøtoøproceedø(Y/N)ø>>>"
LETøconfirm$="ø"
ATø5,58øGETøconfirm$
IFøWHERE(confirm$,"Nn")<>0
øøRELEASEøconfirm$
øøRETURN
ENDIF
CLS
ATø3,26øSAYø"Cleaningøfilesø-øPleaseøwait"
USEøSCPROD
COPYøTOøTEMPøFORøDELETED()=0
USE
DELETEøFILEøSCPROD
RENAMEøTEMPøTOøSCPROD
USEøSCSUPP
COPYøTOøTEMPøFORøDELETED()=0
USE
DELETEøFILEøSCSUPP
RENAMEøTEMPøTOøSCSUPP
USEøSCPROD
RELEASEøconfirm$
RETURN
SCPROD.DEF
* SCPROD.DEF
CODE$,6
DESC$,20
SUPP$,3
SELL_AT
BUY_AT
CASE
VALUE
MINIMUM
STOCK
LUPDATE$,10
BUGFIX$,10
SCSIAM.PRG
* SCSIAM.PRG V1.03 BY DEREK FOUNTAIN
* Amend a products details - Called from SCSIMAIN.PRG
* Following at say must be typed on one line - it is 80 spaces.
ATø7,0øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
øøøøøøøøøø+"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
* The initial data goes into mvars
LETømcode$=1:CODE$
LETømdesc$=1:DESC$
LETømsupp$=1:SUPP$
LETømsell_at=1:SELL_AT
LETømbuy_at=1:BUY_AT
LETømcase=1:CASE
LETømminimum=1:MINIMUM
* Loop while data is not confirmed
LETøconfirm$="N"
DOøWHILEøUPPER(confirm$)="N"
øøATø7,25øSAYø"Amendøeachøfield,øoneøatøaøtime"
øø*øGetøeachøfield
øøATø2,ø5øGETømcode$
øøATø2,35øGETømdesc$
øøATø2,74øGETømsupp$
øøATø4,ø8øGETømsell_at
øøATø4,26øGETømbuy_at
øøATø4,45øGETømcase
øøATø4,71øGETømminimum
* Get confirmation of data
øøATø7,22øSAYø"Pleaseøconfirmøthisødataø(Y/N)ø>>>"
øøLETøconfirm$="ø"
øøDOøWHILEøconfirm$="ø"
øøøøATø7,57øGETøconfirm$øøøøøøø
øøøøIFøWHERE(confirm$,"YNyn")=0
øøøøøøLETøconfirm$="ø"
øøøøENDIF
øøENDDO
øøATø7,22øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
ENDDOøøøøøøøøøøøøøø*øLoopøbackøifønotøconfirmed
* Got confirmed data in mvars, put them over the old data
LETø1:CODE$=mcode$
LETø1:DESC$=mdesc$
LETø1:SUPP$=msupp$
LETø1:SELL_AT=msell_at
LETø1:BUY_AT=mbuy_at
LETø1:CASE=mcase
LETø1:MINIMUM=mminimum
LETø1:LUPDATE$=today$
RELEASEømcode$,mdesc$,msupp$,msell_at,mbuy_at,mcase,mminimum,confirm$
RETURN
SCSIBACK.PRG
* SCSIBACK.PRG V1.00 BY DEREK FOUNTAIN
* Moves back a record in the database
* There is a slight problem with skipping backwards. If the
* user tries to skip back past the first record, the record
* pointer sticks at 1. A check is put in the code to detect this
* Beginning Of File flag is set to 0
LETøbof=0
IFøRECNO()=1
* We are at the beginning of file, so flag it
øøLETøbof=1
ENDIF
SKIPø-1
* If we were at the begining of file, move the other end
IFøbof=1
øøATø7,18øSAYø"Topøoføfileø-øMovingøtoøbottom.øPressøanyøkey"
øøWAITøøøøø
øøGOøBOTTOMøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø* Go to bottom of file if we have
ENDIF
RELEASEøbof
RETURN
SCSIDELE.PRG
* SCSIDELE.PRG V1.01 BY DEREK FOUNTAIN
* Deletes the current record in the database
IFøDELETED()=0øøøøøøøøøøøøøøø* Not already deleted
øøATø7,12øSAYø"Pleaseøconfirmøthisørecordøisøtoøbeødeletedø(Y/N)ø>>>"
øøLETøconfirm$="ø"
øøDOøWHILEøconfirm$="ø"
øøøøATø7,67øGETøconfirm$øøøøøøø
øøøøIFøWHERE(confirm$,"YNyn")=0
øøøøøøLETøconfirm$="ø"
øøøøENDIF
øøENDDO
øøIFøUPPER(confirm$)="Y"
øøøøIFøcalling$="SCSI"
øøøøøøLETø1:LUPDATE$=today$
øøøøENDIF
øøøøDELETEøRECORD
øøENDIF
ENDIF
RELEASEøconfirm$
RETURN
SCSIFIND.PRG
* SCSIFIND.PRG V1.00 BY DEREK FOUNTAIN
* Finds a specified record
ATø2,ø5øSAYø"øøøøøø"
ATø2,35øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
ATø2,74øSAYø"øøø"
ATø4,ø8øSAYø"øøøøøøøø"
ATø4,26øSAYø"øøøøøøøø"
ATø4,45øSAYø"øøøøøøøø"
ATø4,71øSAYø"øøøøøøøø"
LETømcode$="øøøøøø"
ATø2,5øøGETømcode$
IFømcode$<>"ø"
øøATø2,5øSAYø"SEARCHING"
øøLETøloc=RECNO()
øøLOCATEøFORø1:CODE$=mcode$
øøATø2,5øSAYø"øøøøøøøøø"
øøIFøEOF()=1
øøøøATø2,5øSAYø"NOøFINDøø"
øøøøLETøcount=10
øøøøDOøWHILEøcount>0
øøøøøøLETøcount=count-1
øøøøENDDO
øøøøATø2,5øSAYø"øøøøøøøøø"
øøøøGOøloc
øøENDIF
ENDIFøøøøøø
RELEASEømcode$,loc,count
RETURN
SCSIINP.PRG
* SCSIINP.PRG V1.03 BY DEREK FOUNTAIN
* Input of new products details - Called from SCSIMAIN.PRG
ATø7,0øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
*øTheøinitialødataøgoesøintoømvars
LETømcode$="øøøøøø"
LETømdesc$="øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
LETømsupp$="øøø"
LETømsell_at=0.00
LETømbuy_at=0.00
LETømcase=0.00
LETømminimum=0.00
* Loop while data is not confirmed
LETøconfirm$="N"
DOøWHILEøUPPER(confirm$)="N"
øøATø0,0øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
øøATø0,56øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
øøATø2,ø5øSAYø"øøøøøø"
øøATø2,35øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
øøATø2,74øSAYø"øøø"
øøATø4,ø8øSAYø"øøøøøøøøø"
øøATø4,26øSAYø"øøøøøøøøø"
øøATø4,45øSAYø"øøøøøøøøø"
øøATø4,71øSAYø"øøøøøøøøø"
øøATø7,25øSAYø"Enterøeachøfield,øoneøatøaøtime"
* Get each field
øøATø2,ø5øGETømcode$
øøIFømcode$="øøøøøø"
øøøøRELEASEømcode$,mdesc$,msupp$,msell_at,mbuy_at,mcase,mminimum,confirm$
øøøøRETURN
øøENDIF
øøATø2,35øGETømdesc$
øøATø2,74øGETømsupp$
øøATø4,ø8øGETømsell_at
øøATø4,26øGETømbuy_at
øøATø4,45øGETømcase
øøATø4,71øGETømminimum
* Get confirmation of data
øøATø7,21øSAYø"Pleaseøconfirmøthisødataø(Y/N/Q)ø>>>"
øøLETøconfirm$="ø"
øøDOøWHILEøconfirm$="ø"
øøøøATø7,58øGETøconfirm$øøøøøøø
øøøøIFøWHERE(confirm$,"YNQynq")=0
øøøøøøLETøconfirm$="ø"
øøøøENDIF
øøENDDO
øøIFøUPPER(confirm$)="Q"
øøøøRELEASEømcode$,mdesc$,msupp$,msell_at,mbuy_at,mcase,mminimum,confirm$
øøøøRETURN
øøENDIF
øøATø7,21øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
ENDDOøøøøøøøøøøøøøø*øLoopøbackøifønotøconfirmed
* Got confirmed data in mvars, put them into a new record
APPENDøBLANK
LETø1:CODE$=mcode$
LETø1:DESC$=mdesc$
LETø1:SUPP$=msupp$
LETø1:SELL_AT=msell_at
LETø1:BUY_AT=mbuy_at
LETø1:CASE=mcase
LETø1:MINIMUM=mminimum
LETø1:LUPDATE$=today$
RELEASEømcode$,mdesc$,msupp$,msell_at,mbuy_at,mcase,mminimum,confirm$
RETURN
SCSIMAIN.PRG
* SCSIMAIN.PRG V1.09 BY DEREK FOUNTAIN
* Maintenance of products file - Called by SCSTART.PRG
CLS
USEøSCPROD
* Set up screen
ATø0,26øSAYø"PRODUCTøDATAøFILEøMAINTENANCE"
ATø2,0øSAYø"CODE:"
ATø2,30øSAYø"ITEM:"
ATø2,60øSAYø"SUPPLIERøCODE:"
ATø4,0øSAYø"SELLøAT:"
ATø4,19øSAYø"BUYøAT:"
ATø4,40øSAYø"CASE:"
ATø4,57øSAYø"MINIMUMøSTOCK:"
*øForøtheøbenefitøoføtheødeleteøroutines...
LETøcalling$="SCSI"
* Infinite loop, keep getting choices
DOøWHILEø1=1
* Print up the current record
øøATø0,65øSAYø"DATED:"
øøATø2,ø5øSAYø"øøøøøø"
øøATø2,35øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
øøATø2,74øSAYø"øøø"
øøATø4,ø8øSAYø"øøøøøøøøø"
øøATø4,26øSAYø"øøøøøøøøø"
øøATø4,45øSAYø"øøøøøøøøø"
øøATø4,71øSAYø"øøøøøøøøø"
øøATø0,71øSAYø1:LUPDATE$
øøATø2,5øSAYø1:CODE$
øøATø2,35øSAYø1:DESC$
øøATø2,74øSAYø1:SUPP$
øøATø4,8øSAYø1:SELL_AT
øøATø4,26øSAYø1:BUY_AT
øøATø4,45øSAYø1:CASE
øøATø4,71øSAYø1:MINIMUM
øøIFøDELETED()=1øø
øøøøATø0,0øSAYø"DELETEDøRECORD"
øøøøATø7,10øSAYø"(N)ext,(B)ack,(F)ind,(R)ecall,(I)nput,(A)mendøorø(Q)uitø>>>"
øøELSE
øøøøATø0,0øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"ø
øøøøATø7,10øSAYø"(N)ext,(B)ack,(F)ind,(D)elete,(I)nput,(A)mendøorø(Q)uitø>>>"
øøENDIF
* Get a valid choice
øøLETøchoice$="ø"
øøDOøWHILEøchoice$="ø"
øøøøATø7,70øGETøchoice$
øøøøIFøWHERE(UPPER(choice$),"NBFDRIAQ")=0
øøøøøøLETøchoice$="ø"
øøøøENDIF
øøENDDO
* Clear prompt form bottom line
øøATø7,10øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
øøIFøUPPER(choice$)="Q"øøøøøøøøøøø* Option was to quit
øøøøRELEASEøcalling$
øøøøRETURN
øøENDIF
øøIFøUPPER(choice$)="N"øøøøøøøøøøø* Option was Next record
øøøøDOøSCSINEXT.PRG
øøENDIF
øøIFøUPPER(choice$)="B"øøøøøøøøøøø* Choice was to move Back a record
øøøøDOøSCSIBACK.PRG
øøENDIF
øøIFøUPPER(choice$)="I"øøøøøøøøøøø* Choice was to input a new record
øøøøDOøSCSIINP.PRG
øøENDIF
øøIFøUPPER(choice$)="A"øøøøøøøøøøø* Choice was to amend current record
øøøøDOøSCSIAM.PRG
øøENDIF
øøIFøUPPER(choice$)="F"øøøøøøøøøøø* Choice was Find
øøøøDOøSCSIFIND.PRG
øøENDIF
øøIFøUPPER(choice$)="D"øøøøøøøøøøø* Choice was delete
øøøøDOøSCSIDELE.PRG
øøENDIF
øøIFøUPPER(choice$)="R"øøøøøøøøøøø* Choice was recall
øøøøDOøSCSIRECA.PRG
øøENDIF
ENDDO
SCSINEXT.PRG
* SCSINEXT.PRG V1.00 BY DEREK FOUNTAIN
* Skips to next record in database
SKIP
IFøEOF()=1øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø* Check we haven't skipped to far
øøATø7,19øSAYø"Endøoføfileø-øMovingøtoøtop.øPressøanyøkey"
øøWAIT
øøGOøTOPøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø* Back to the top if we have
ENDIF
RETURN
SCSIRECA.PRG
* SCSIRECA.PRG V1.01 BY DEREK FOUNTAIN
* Recalls the current record in the database
IFøDELETED()=1øøøøøøøøøøøøøøø* Must be deleted already
øøATø7,12øSAYø"Pleaseøconfirmøthisørecordøisøtoøbeørecalledø(Y/N)ø>>>"
øøLETøconfirm$="ø"
øøDOøWHILEøconfirm$="ø"
øøøøATø7,68øGETøconfirm$
øøøøIFøWHERE(confirm$,"YNyn")=0
øøøøøøLETøconfirm$="ø"
øøøøENDIF
øøENDDO
øøIFøUPPER(confirm$)="Y"
øøøøIFøcalling$="SCSI"
øøøøøøLETø1:LUPDATE$=today$
øøøøENDIF
øøøøRECALLøRECORD
øøENDIF
ENDIF
RELEASEøconfirm$
RETURN
SCSTART.PRG
* SCSTART.PRG V1.04 BY DEREK FOUNTAIN
CLS
ATø0,24øSAYø"WORDMONGERSøSTOCKøCONTROLøSYSTEM"
LETøtoday$="øøøøøøøø"
ATø3,21øSAYø"Pleaseøenterøtodaysødateø>>>"
ATø3,50øGETøtoday$
DOøWHILEø1=1
øøCLS
øøATø0,24øSAYø"WORDMONGERSøSTOCKøCONTROLøSYSTEM"
øøATø2,16øSAYø"1)øSTOCKøCHECKøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø5)øSUPPLIERSøFILEøREPORT"
øøATø3,16øSAYø"2)øPRODUCTSø-øENTER/AMENDøøøø6)øSTOCKøVALUATION"
øøATø4,16øSAYø"3)øSUPPLIERSø-øENTER/AMENDøøø7)øCLEANøFILES"
øøATø5,16øSAYø"4)øPRODUCTSøFILEøREPORTøøøøøø8)øEXITøSYSTEM"
øøATø7,30øSAYø"PLEASEøSELECTø>>>"
øøLETøchoice$="ø"
øøDOøWHILEøchoice$="ø"
øøøøATø7,48øGETøchoice$øøøø
øøøøIFøWHERE(choice$,"12345678")=0
øøøøøøLETøchoice$="ø"
øøøøENDIF
øøENDDO
øøIFøchoice$="1"
øøøøDOøSCSTOCK.PRG
øøENDIF
øøIFøchoice$="2"
øøøøDOøSCSIMAIN.PRG
øøENDIF
øøIFøchoice$="3"
øøøøDOøSCSUMAIN.PRG
øøENDIF
øøIFøchoice$="4"
øøøøDOøSCOUTPRO.PRG
øøENDIF
øøIFøchoice$="5"
øøøøDOøSCOUTSUP.PRG
øøENDIF
øøIFøchoice$="6"
øøøøDOøSCSTKREP.PRG
øøENDIF
øøIFøchoice$="7"
øøøøDOøSCPACK.PRG
øøENDIF
øøIFøchoice$="8"
øøøøATø5,0øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø4)øPR"ø
øøøøQUIT
øøENDIF
ENDDO
SCSTKREP.PRG
* SCSTKREP.PRG V1.01 BY DEREK FOUNTAIN
* Outputs a stock report to the specified file
* Uses a new file with one very large field to dump the data
CLS
ATø0,34øSAYø"STOCKøREPORT"
ATø2,19øSAYø"Thisøreportøinvolvesøgeneratingøaøworkøfile"
ATø3,25øSAYø"Thisøprocessømayøtakeøsomeøtime"
ATø5,8øSAYø"Pleaseøconfirmøyouøwishøtoøgenerateøtheøreportøfileø(Y/N)ø>>>"
LETøconfirm$="ø"
ATø5,70øGETøconfirm$
IFøUPPER(confirm$)="N"
øøRELEASEøconfirm$
øøRETURN
ENDIF
CLS
ATø0,34øSAYø"STOCKøREPORT"
ATø3,24øSAYø"Creatingøworkøfileø-øPleaseøwait"
SELECTø2
CREATEøREPøFROMøREP.DEF
SELECTø1
USEøSCPROD
GOøTOP
DOøWHILEøEOF()=0
øøSELECTø2
øøAPPENDøBLANK
øøSELECTø1
øøLETømline$=1:CODE$+"ø"+1:DESC$+"ø"
øøLETømsupp$=1:SUPP$
øøLETøloc=RECNO()
øøUSEøSCSUPPøø
øøLOCATEøFORø1:SUPP$=msupp$
øøLETømsupp$=1:NAME$
øøIFøEOF()=1
øøøøLETømsupp$="Supplierønotøonøfileøøøøø"
øøENDIF
øøUSEøSCPROD
øøGOøloc
øøLETøvar1=1:BUY_AT
øøLETølvar1=LEN("&var1")
øøLETøvar2=1:SELL_AT
øøLETølvar2=LEN("&var2")
øøLETøvar3=1:VALUE
øøLETølvar3=LEN("&var3")
øøLETøvar4=1:STOCK
øøLETølvar4=LEN("&var4")
øøLETølmsupp=LEN(TRIM(msupp$))
øøLETø2:LINE$=mline$+"ø"+msupp$
øøLETø2:LINE$=TRIM(2:LINE$)+
øøøøøøSUBSTR("øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø",1,25-lmsupp)+"ø&var1"
øøLETø2:LINE$=TRIM(2:LINE$)+SUBSTR("øøøøøøøøøø",1,10-lvar1)+"ø&var2"
øøLETø2:LINE$=TRIM(2:LINE$)+SUBSTR("øøøøøøøøøø",1,10-lvar2)+"ø&var3"
øøLETø2:LINE$=TRIM(2:LINE$)+SUBSTR("øøøøøøøøøø",1,10-lvar3)+"ø&var4"
øøLETø2:LINE$=TRIM(2:LINE$)+SUBSTR("øøøøøøøøøø",1,10-lvar4)+"ø"+1:LUPDATE$
øøSKIP
ENDDO
SELECTø2
GOøTOP
ATø3,24øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
DOøWHILEø1=1
øøATø2,20øSAYø"Pleaseøenterøtheønameøoføtheøoutputøfile"
øøLETøfilenam$="øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
øøATø6,25øSAYø"Leaveøtheønameøblankøtoøabandon"
øøATø4,30øGETøfilenam$øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø
øøIFøfilenam$="ø"
øøøøUSE
øøøøDELETEøFILEøREP
øøøøSELECTø1
øøøøRELEASEøconfirm$,msupp$,filenam$,over$,mline$,loc
øøøøRELEASEøvar1,var2,var3,var4,lvar1,lvar2,lvar3,lvar4
øøøøRETURN
øøENDIF
øøATø2,20øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
øøATø4,30øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø
øøATø6,25øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
øøLETøover$="Y"
øøIFøFILE(filenam$)=1
øøøøATø3,20øSAYø"Fileøexistsø-øOverwriteøit?ø(Y/N)ø>>>"
øøøøLETøover$="ø"
øøøøDOøWHILEøover$="ø"
øøøøøøATø3,59øGETøover$
øøøøøøIFøWHERE(over$,"YyNn")=0
øøøøøøøøLETøover$="ø"
øøøøøøENDIF
øøøøENDDO
øøENDIF
øøATø3,20øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
øøIFøUPPER(over$)="Y"
øøøøATø3,20øSAYø"CopyingødataøtoøPipedreamøfileø"+filenam$
øøøøCOPYøTOø&filenam$øPD
øøøøATø3,20øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
øøøøATø3,11øSAYø"Processøcompletedø-øTheøfileøMUSTøbeøloadedøasøplainøtext"
øøøøATø5,27øSAYø"Pressøanyøkeyøtoøcontinue"
øøøøWAIT
øøøøUSE
øøøøDELETEøFILEøREP
øøøøSELECTø1
øøøøRELEASEøconfirm$,msupp$,filenam$,over$,mline$,loc
øøøøRELEASEøvar1,var2,var3,var4,lvar1,lvar2,lvar3,lvar4
øøøøRETURN
øøENDIF
ENDDO
SCSTOCK.PRG
* SCSTOCK.PRG V1.05 BY DEREK FOUNTAIN
* THIS ROUTINE ALLOWS UPDATE OF THE NUMBER OF A SELECTED ITEM
* IN STOCK
CLS
ATø0,30øSAYø"STOCKøUPDATEøROUTINE"
USEøSCPRODøøøøøøøøøøø* Products database
DOøWHILEø1=1øøøøøøøøø* Infinite loop
øøLETømcode$="øøøøøø"
øøLETømdesc$="øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
øøATø2,0øSAYø"CODE:øøøøøø"
øøATø2,30øSAYø"ITEM:øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
øøATø2,60øSAYø"SUPPLIERøCODE:øøø"
øøATø4,0øSAYø"SELLINGøPRICE:øøøøøøøøø"
øøATø4,30øSAYø"BUYINGøPRICE:øøøøøøøøø"
øøATø4,60øSAYø"NOøPERøCASE:øøøøøøøøø"
øøATø6,0øSAYø"CURRENTøSTOCK:øøøøøøøøø"
øøATø6,30øSAYø"MINIMUMøSTOCK:øøøøøøøøø"
øøATø6,60øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
øøATø2,5øGETømcode$
øøIFømcode$="øøøøøø"
øøøøRELEASEømcode$,p,mcases,msingles
øøøøRETURN
øøENDIF
øøIFømcode$="?"
øøøøATø2,5øSAYø"øøøøøøø"
øøøøATø2,35øGETømdesc$
øøøøIFømdesc$="ø"
øøøøøøRETURN
øøøøENDIF
øøøøLOCATEøFORøUPPER(1:DESC$)=UPPER(TRIM(mdesc$))ø
øøELSE
øøøøLOCATEøFORø1:CODE$=mcode$øø
øøENDIF
øøIFøEOF()=1
øøøøATø2,5øSAYø"NOøFIND"
øøøøLETøp=30
øøøøDOøWHILEøp>0
øøøøøøLETøp=p-1
øøøøENDDO
øøøøATø2,35øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
øøøøATø2,5øSAYø"øøøøøøø"
øøøøLETømcode$="øøøøøø"
øøENDIF
øøIFømcode$<>"øøøøøø"
øøøøATø2,5øSAYø1:CODE$
øøøøATø2,35øSAYø1:DESC$
øøøøATø2,74øSAYø1:SUPP$
øøøøATø4,15øSAYø1:SELL_AT
øøøøATø4,43øSAYø1:BUY_AT
øøøøATø4,72øSAYø1:CASE
øøøøATø6,14øSAYø1:STOCK
øøøøATø6,44øSAYø1:MINIMUM
øøøøIFømcode$="?"
øøøøøøLETøconfirm$="Y"
øøøøøøATø7,13øSAYø"Pleaseøconfirmøthisøisøtheøcorrectøproductø(Y/N)ø>>>"
øøøøøøATø7,66øGETøconfirm$
øøøøøøATø7,13øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
øøøøøøIFøUPPER(confirm$)="N"
øøøøøøøøENDDO
øøøøøøENDIF
øøøøENDIF
øøøøLETømcases=0
øøøøLETømsingles=0
øøøøATø6,62øSAYø"CASES?:"
øøøøATø6,69øGETømcases
øøøøATø6,60øSAYø"SINGLES?:"
øøøøATø6,69øSAYø"øøøøøøøø"
øøøøATø6,69øGETømsingles
øøøøLETø1:STOCK=mcases*1:CASE+msingles
øøøøLETø1:VALUE=1:STOCK*1:SELL_AT
øøøøLETø1:LUPDATE$=today$
øøENDIF
ENDDO
SCSUAM.PRG
* SCSUAM.PRG V1.01 BY DEREK FOUNTAIN
* Amend of suppliers details - Called from SCSUMAIN.PRG
ATø7,0øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
* The initial data goes into mvars
LETømsupp$=1:SUPP$
LETømname$=1:NAME$
LETømcontact$=1:CONTACT$
LETømphone$=1:PHONE$
LETømadd1$=1:ADD1$
LETømadd2$=1:ADD2$
LETømadd3$=1:ADD3$
LETømadd4$=1:ADD4$
* Loop while data is not confirmed
LETøconfirm$="N"
DOøWHILEøUPPER(confirm$)="N"
øøATø7,25øSAYø"Amendøeachøfield,øoneøatøaøtime"
øø*øGetøeachøfield
øøATø2,12øGETømname$
øøATø3,12øGETømsupp$
øøATø4,12øGETømcontact$
øøATø5,12øGETømphone$
øøATø2,48øGETømadd1$
øøATø3,48øGETømadd2$
øøATø4,48øGETømadd3$
øøATø5,48øGETømadd4$
* Get confirmation of data
øøATø7,22øSAYø"Pleaseøconfirmøthisødataø(Y/N)ø>>>"
øøLETøconfirm$="ø"
øøDOøWHILEøconfirm$="ø"
øøøøATø7,57øGETøconfirm$øøøøøøø
øøøøIFøWHERE(confirm$,"YNyn")=0
øøøøøøLETøconfirm$="ø"
øøøøENDIF
øøENDDO
øøATø7,21øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
ENDDOøøøøøøøøøøøøøø* Loop back if not confirmed
* Got confirmed data in mvars, put them over the old data
LETø1:SUPP$=msupp$
LETø1:NAME$=mname$
LETø1:CONTACT$=mcontact$ø
LETø1:PHONE$=mphone$
LETø1:ADD1$=madd1$
LETø1:ADD2$=madd2$
LETø1:ADD3$=madd3$
LETø1:ADD4$=madd4$
RELEASEømsupp$,mname$,mcontact$,mphone$,madd1$,madd2$,madd3$,madd4$,confirm$
RETURN
SCSUFIND.PRG
* SCSUFIND.PRG V1.01 BY DEREK FOUNTAIN
* Finds a specified record
ATø2,11øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
ATø3,11øSAYø"øøøøø"
ATø4,11øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
ATø5,11øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
ATø2,48øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
ATø3,48øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
ATø4,48øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
ATø5,48øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
LETømsupp$="øøø"
ATø3,12øGETømsupp$
IFømsupp$<>"ø"øøøø
øøATø3,12øSAYø"SEARCHING"
øøLETøloc=RECNO()
øøLOCATEøFORø1:SUPP$=msupp$
øøATø3,12øSAYø"øøøøøøøøø"
øøIFøEOF()=1
øøøøATø3,12øSAYø"NOøFINDøø"
øøøøLETøcount=10
øøøøDOøWHILEøcount>0
øøøøøøLETøcount=count-1
øøøøENDDO
øøøøATø3,12øSAYø"øøøøøøøøø"
øøøøGOøloc
øøENDIF
ENDIFøøøøøø
RELEASEømsupp$,loc,count
RETURN
SCSUINP.PRG
* SCSUINP.PRG V1.01 BY DEREK FOUNTAIN
* Input of new suppliers details - Called from SCSUMAIN.PRG
ATø7,0øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
* The initial data goes into mvars
LETømsupp$="øøø"
LETømname$="øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
LETømcontact$="øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
LETømphone$="øøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
LETømadd1$="øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
LETømadd2$="øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
LETømadd3$="øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
LETømadd4$="øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
* Loop while data is not confirmed
LETøconfirm$="N"
DOøWHILEøUPPER(confirm$)="N"
øøATø2,11øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
øøATø3,11øSAYø"øøøøø"
øøATø4,11øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
øøATø5,11øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
øøATø2,48øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
øøATø3,48øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
øøATø4,48øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
øøATø5,48øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
øøATø7,25øSAYø"Enterøeachøfield,øoneøatøaøtime"
øø*øGetøeachøfield
øøATø2,12øGETømname$
øøIFømname$="øøøøøø"
øøøøRELEASEømsupp$,mname$,mcontact$,mphone$
øøøøRELEASEømadd1$,madd2$,madd3$,madd4$,confirm$
øøøøRETURN
øøENDIF
øøATø3,12øGETømsupp$
øøATø4,12øGETømcontact$
øøATø5,12øGETømphone$
øøATø2,48øGETømadd1$
øøATø3,48øGETømadd2$
øøATø4,48øGETømadd3$
øøATø5,48øGETømadd4$
* Get confirmation of data
øøATø7,21øSAYø"Pleaseøconfirmøthisødataø(Y/N/Q)ø>>>"
øøLETøconfirm$="ø"
øøDOøWHILEøconfirm$="ø"
øøøøATø7,58øGETøconfirm$øøøøøøø
øøøøIFøWHERE(confirm$,"YNQynq")=0
øøøøøøLETøconfirm$="ø"
øøøøENDIF
øøENDDO
øøIFøUPPER(confirm$)="Q"
øøøøRELEASEømsupp$,mname$,mcontact$,mphone$
øøøøRELEASEømadd1$,madd2$,madd3$,madd4$,confirm$
øøøøRETURN
øøENDIF
øøATø7,21øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
ENDDOøøøøøøøøøøøøøø* Loop back if not confirmed
* Got confirmed data in mvars, put them into a new record
APPENDøBLANK
LETø1:SUPP$=msupp$
LETø1:NAME$=mname$
LETø1:CONTACT$=mcontact$
LETø1:PHONE$=mphone$
LETø1:ADD1$=madd1$
LETø1:ADD2$=madd2$
LETø1:ADD3$=madd3$
LETø1:ADD4$=madd4$
RELEASEømsupp$,mname$,mcontact$,mphone$,madd1$,madd2$,madd3$,madd4$,confirm$
RETURN
SCSUMAIN.PRG
* SCSUMAIN.PRG V1.02 BY DEREK FOUNTAIN
* Maintenance of suppliers file - Called by SCSTART.PRG
CLS
USEøSCSUPP
* Set up screen
ATø0,25øSAYø"SUPPLIERSøDATAøFILEøMAINTENANCE"
ATø2,2øSAYø"SUPPLIER:"
ATø3,2øSAYø"CODEøøøø:"
ATø4,2øSAYø"CONTACTø:"
ATø5,2øSAYø"PHONEøøø:"
ATø2,40øSAYø"ADDRESS:"
* Infinite loop, keep getting choices
LETøcalling$="SCSU"
DOøWHILEø1=1
øø*øPrintøupøtheøcurrentørecord
øøATø2,11øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
øøATø3,11øSAYø"øøøøø"
øøATø4,11øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
øøATø5,11øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
øøATø2,48øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
øøATø3,48øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
øøATø4,48øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
øøATø5,48øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
øøATø2,12øSAYø1:NAME$
øøATø3,12øSAYø1:SUPP$
øøATø4,12øSAYø1:CONTACT$
øøATø5,12øSAYø1:PHONE$
øøATø2,48øSAYø1:ADD1$
øøATø3,48øSAYø1:ADD2$
øøATø4,48øSAYø1:ADD3$
øøATø5,48øSAYø1:ADD4$
øøIFøDELETED()=1øø
øøøøATø0,0øSAYø"DELETEDøRECORD"
øøøøATø7,10øSAYø"(N)ext,(B)ack,(F)ind,(R)ecall,(I)nput,(A)mendøorø(Q)uitø>>>"
øøELSE
øøøøATø0,0øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"ø
øøøøATø7,10øSAYø"(N)ext,(B)ack,(F)ind,(D)elete,(I)nput,(A)mendøorø(Q)uitø>>>"
øøENDIF
* Get a valid choice
øøLETøchoice$="ø"
øøDOøWHILEøchoice$="ø"
øøøøATø7,70øGETøchoice$
øøøøIFøWHERE(UPPER(choice$),"NBFDRIAQ")=0
øøøøøøLETøchoice$="ø"
øøøøENDIF
øøENDDO
* Clear prompt form bottom line
øøATø7,10øSAYø"øøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø"
øøIFøUPPER(choice$)="Q"øøøøøøøøøø* Option was to quit
øøøøRELEASEøcalling$
øøøøRETURN
øøENDIF
øøIFøUPPER(choice$)="N"øøøøøøøøøø* Option was Next record
øøøøDOøSCSINEXT.PRGøøøøøøøøøøøøøø* This is the same routine as in
øøENDIFøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø* the stock file maintenance
øøIFøUPPER(choice$)="B"øøøøøøøøøø* Choice was to move Back a record
øøøøDOøSCSIBACK.PRGøøøøøøøøøøøøøø*øDitto
øøENDIF
øøIFøUPPER(choice$)="I"øøøøøøøøøø* Choice was to input a new record
øøøøDOøSCSUINP.PRG
øøENDIF
øøIFøUPPER(choice$)="A"øøøøøøøøøø* Choice was to amend current record
øøøøDOøSCSUAM.PRG
øøENDIF
øøIFøUPPER(choice$)="F"øøøøøøøøøø* Choice was Find
øøøøDOøSCSUFIND.PRG
øøENDIF
øøIFøUPPER(choice$)="D"øøøøøøøøøø* Choice was delete
øøøøDOøSCSIDELE.PRGøøøøøøøøøøøøøø* Same routine as used in the stock
øøENDIFøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøøø* item maintenance
øøIFøUPPER(choice$)="R"øøøøøøøøøø* Choice was recall
øøøøDOøSCSIRECA.PRGøøøøøøøøøøøøøø* Ditto
øøENDIF
ENDDO
SCSUPP.DEF
* SCSUPP.DEF
SUPP$,3
NAME$,25
ADD1$,25
ADD2$,25
ADD3$,25
ADD4$,25
PHONE$,15
CONTACT$,25