This page is live and is not completed yet!
This section is currently being changed and re-written. It is very nearly finished.
Introduction
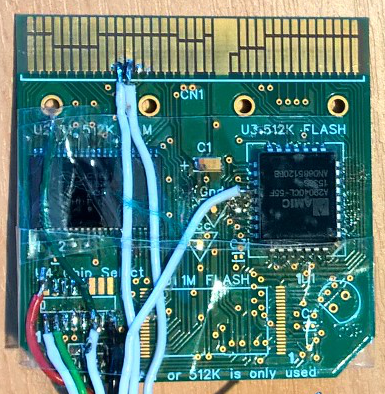
The Z88 Flash/RAM card has been working for several years now. When OZ 4.6 was introduced, allowing applications to be run in RAM, some games failed to run.
| Standard Version | RAM Version | FLASH Version |
|---|---|---|
This was thought to be due to an intermittent timing error from the decode chip CD74HCT139 which switches between the RAM and Flash chip but after the Z88 Hardware Investigation, it has been discovered to be a misunderstanding by both the hardware and software engineers on how to write faultlessly to the flash chip. This has only affected a few users, i.e. those who play games in RAM or who do repetitive writing to the flash card. The majority of users have not reported any problems.
Object
It has already been proved that if OZ 4.7 is run in a 256K EPROM card, the application runs faultlessly. This is because the code that the flash chip normally writes to the data bus is no longer written, as there is no flash chip. The OTP (One Time Programming) EPROM uses a similar footprint to the 512K Flash chip, so it was decided to try this combination and see if it improves the performance.
Two versions are being considered.
- 256K - for OZ 4.7 and
768K of RAM - 256K - for OZ 4.7 and
768K of Flash
Although the best solution would be a software upgrade to OZ 4.7 allowing users to update their cards, it has been decided to see if by changing the hardware the same result may be achieved. See Writing to Flash Chips for a full explanation of what needs to be fixed. The object of this exercise is to run OZ 4.7 in the OTP EPROM in the top 256K area, leaving the rest of the address space 768K for either RAM, using the 1M RAM chip or Flash, using the 1M Flash chip. The only disadvantage is that users will no longer be able to update their OZ themselves. A socket is fitted in the card, so that the OTP EPROM may be replaced.
The address decoding will be identical for both versions.
The modified 512K/512K card has already been used with the modified extender card as described in the Z88 Hardware Investigation section, to test how the decoder chip may be used with different address maps. It was decided just to build a card using the knowledge gained from these previous tests.
Decoder Details
The same decoding algorithm is used for both cards. The output is either connected to the CE of the RAM or FLASH chip.
256K OTP EPROM, 768K FLASH or RAM
| CE | A19 | A18 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 256K OTP EPROM | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 768K FLASH or RAM | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 768K FLASH or RAM | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 768K FLASH or RAM | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| NOT SELECTED | 1 | X | X. |
Decoder Connections
The decode chip used, is repeated twice in the same device. The first device decodes the 256K EPROM with SE1, A19 and A18. The unused decoder is used to select the remainder of the address space, when the card is selected but not the 256K EPROM. The output going to either the RAM or FLASH chip enable.
Selecting the decoder outputs
| I/O | PIN No | I/O | PIN No | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FROM Z88 SE1 | I | E | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | FROM Z88 SE1 (0) | I | E | 15 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| FROM Z88 MA19 | I | A0 | 2 | X | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | FROM OTP EPROM CE (1) | I | A0 | 14 | X | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| FROM Z88 MA18 | I | A1 | 3 | X | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | LOGIC 0 - 0v | I | A1 | 13 | X | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| O | Y0 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | O | Y0 | 12 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |||
| O | Y1 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | TO RAM or FLASH CE | O | Y1 | 11 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| O | Y2 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | O | Y2 | 10 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |||
| TO OTP EPROM CE | O | Y3 | 7 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | O | Y3 | 9 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Using the signal that we wish to control as the Enable signal, choosing which output is used is determined by A0 and A1. In this case they are both high, which means that Y3 is used.
- SE1 to E (Pin 1)
- MA19 (Pin 2) for A19 high
- MA18 (Pin 3) for A18 high
The output for the OTP EPROM CE is Y3 (Pin 7).
The same technique is repeated for
- SE1 to E (Pin 15)
- From OTP EPROM CE to A0 (Pin 14) for when it is high, the OTP is not selected
- GND to A1 (Pin 13) for logic 0
The output for the RAM or Flash is Y1 (Pin 11).
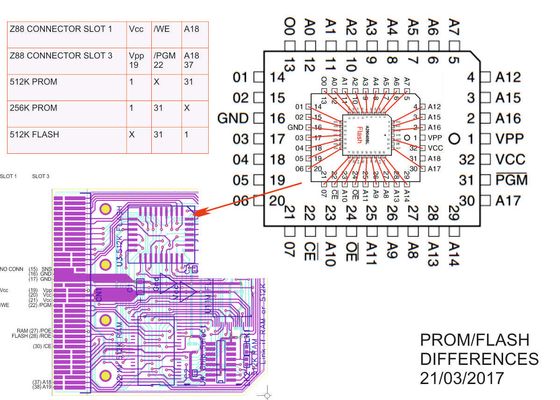
U3 Variants
U3 is currently wired up for a 512K Flash chip. There are 3 signals that use 2 different pins on the PLCC footprint.
These are displayed in the following table.
If links are to be used on a future designed board the following layout maybe considered
| From edge connector | Vpp (19) | A18 (37) | /PGM (22) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| To U3 PLCC Footprint | Pin 1 | Pin 31 | |||
| 512K PROM | |||||
| 256K PROM | |||||
| 512k FLASH |
The 256K PROM is being used
Vpp needs to be connected to pin 1
PGM is already connected to pin 31
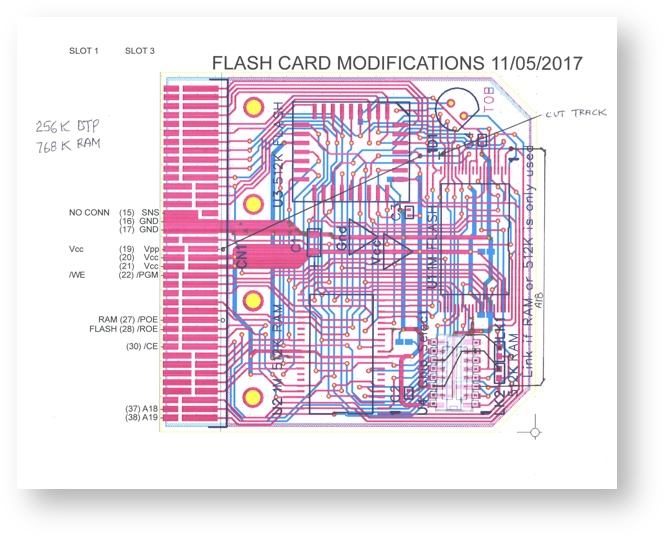
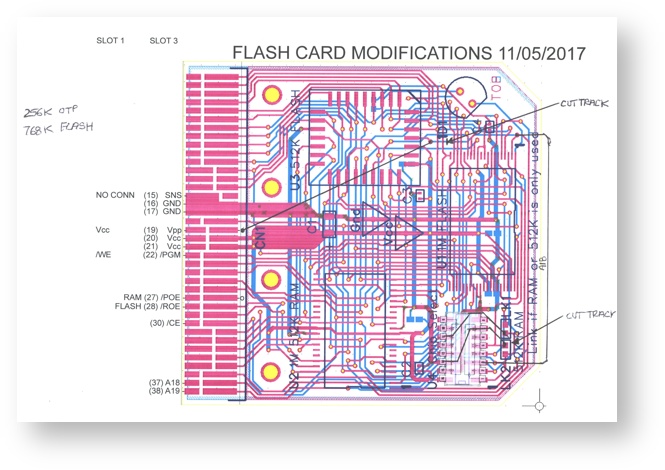
PCB Modifications
Connection Chart
| Edge Con | Decoder | Signal | OTP EPROM | 1M RAM | 1M Flash | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 1 | SE1 | EXISTING CONNECTION | |||
| 38 | 2 | A19 | EXISTING CONNECTION | |||
| 37 | 3 | A18 | ||||
| 7 | 14 | OTP CE | 22 | RH 512K LK | RH 512K LK | |
| 11 | RAM CE | RH RAM LK | ||||
| 11 | FLASH CE | LH RAM LK | ||||
256K OTP EPROM 768 RAM Modifications
| Pin | Pin | Pin | Pin | Pin | Instructions | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reinstate POE/ROE mods they are no longer needed. | |||||||
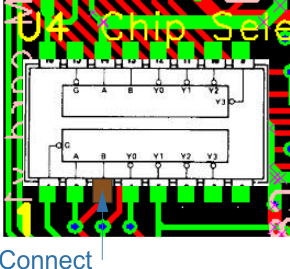
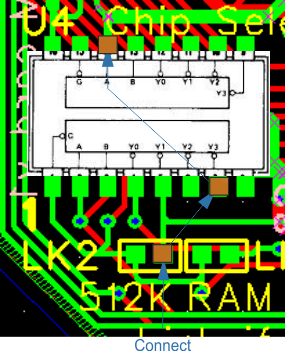
| U4 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 14 | 15 | Lift up pins DO NOT CONNECT TO PCB | |
| U4 | 1 | 2 | 6-8 | 9-13 | 16 | Solder chip to board using the remaining pins | |
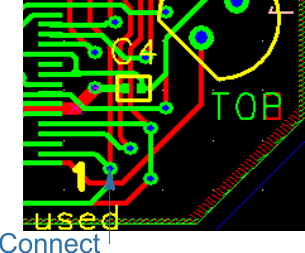
| U4 | 3 | A18 - Connect wire from Pin 3 | |||||
| U1 | to via near 1 U1 | ||||||
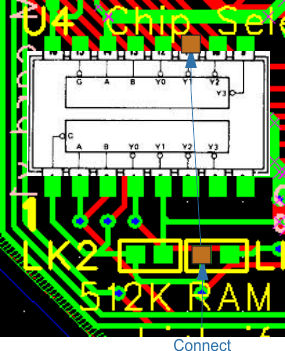
| U4 | 7 | 14 | Connect wire from Pin 7, 14 to RH pad of 512K | ||||
| U4 | 11 | Connect to RH pad of RAM NOTE: This is for the RAM. | |||||
| U3 | Fit socket for U3 | ||||||
| U3 | 1 | Cut track (A18) | |||||
| U3 | 1 | Connect to Vpp Edge connector Pin 19 | |||||
| LK1 - LK2 |
256K OTP EPROM 768 FLASH Modifications
| Pin | Pin | Pin | Pin | Pin | Instructions | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reinstate POE/ROE mods they are no longer needed. | |||||||
| U4 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 14 | 15 | Lift up pins DO NOT CONNECT TO PCB | |
| U4 | 1 | 2 | 6-8 | 9-13 | 16 | Solder chip to board using the remaining pins | |
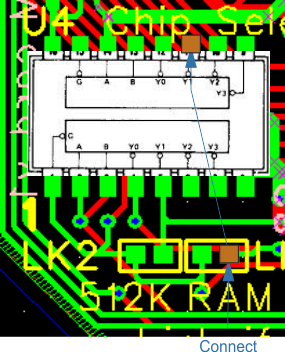
| U4 | 3 | A18 - Connect wire to | |||||
| U1 | via near 1 U1 | ||||||
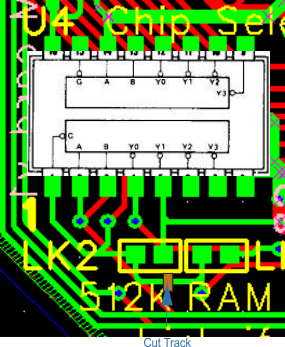
| U4 | 7 | 14 | Connect to RH pad of 512K | ||||
| U4 | 11 | Connect to LH pad of RAM | |||||
| LK1 - LK2 | Cut track between LH pad of 512 and LH pad of RAM | ||||||
| U3 | Fit socket for U3 | ||||||
| U3 | 1 | Cut track (A18) | |||||
| U3 | 1 | Connect to Vpp Edge connector Pin 19 |
Conclusion
Further testing will be done before reporting that a hardware solution has been found.